GeoWebCache
GeoWebCache is a high-performance, tile-caching server designed specifically for accelerating the delivery of geospatial map data over the web. It functions as a critical middleware component that sits between a map server (such as GeoServer, MapServer, or ArcGIS Server) and a map client (like OpenLayers, Leaflet, or MapLibre). By generating, storing, and serving pre-rendered map image tiles in standard web formats (PNG, JPEG, vector tiles), it dramatically reduces server load and improves response times for end users. Unlike rendering maps dynamically for each request, GeoWebCache serves pre-computed tiles, making it an essential tool for building scalable, fast, and responsive web mapping applications that serve large volumes of concurrent users.
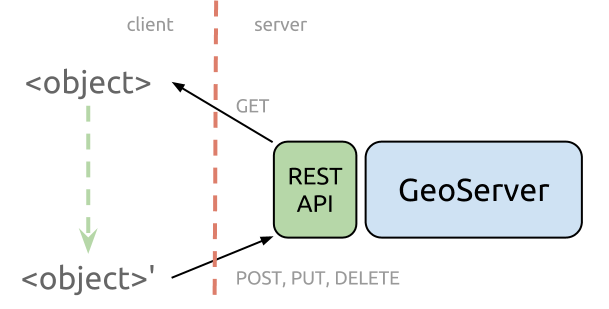
2026-02-11 14:18:10GeoServer REST API
GeoServer REST API is a comprehensive programmatic interface for configuring and managing the GeoServer open-source geospatial data server. As an integral component of the GeoServer software suite, the API provides a standardized HTTP-based mechanism to automate and control virtually all administrative and data publishing tasks within a GeoServer instance. It enables developers, system administrators, and GIS professionals to interact with GeoServer programmatically—creating workspaces, adding data stores, publishing layers, configuring styles (SLD), managing security, and adjusting service settings (WMS, WFS, WCS) without using the web administration interface. This API is essential for integrating GeoServer into automated DevOps pipelines, multi-instance deployments, and custom geospatial application backends.
2026-02-11 14:01:51Space Oblique Mercator (SOM) Projection
Space Oblique Mercator (SOM) Projection is a sophisticated, specialized map projection designed specifically for mapping the continuous surface coverage of Earth-observing satellites in near-polar, sun-synchronous orbits. Conceived in the 1970s by Alden P. Colvocoresses and later refined by John L. Junkins, John P. Snyder, and others, it solves a unique problem: accurately representing the curved, swath-based ground track of a satellite moving in space while the Earth rotates beneath it. Unlike traditional projections that treat the Earth as static relative to the Sun, the SOM mathematically models the dynamic relationship between the satellite's orbital path and the Earth's rotation, creating a nearly conformal map where the satellite's ground track is represented as a straight line with minimal scale distortion along the swath.
2026-02-11 13:52:04General Perspective Projection
General Perspective Projection is a family of azimuthal map projections that simulate the view of the Earth from an arbitrary point in space, creating a perspective effect akin to a photograph taken from a distant observer. Unlike orthographic or stereographic projections which assume specific viewing distances or geometric relationships, this projection allows flexible positioning of the projection point—either above the Earth's surface (for satellite or aerial views) or at an infinite distance. It is particularly valuable for visualizing planetary bodies from space missions, generating realistic global and regional views, and supporting applications in astronomy, remote sensing, and scientific visualization where naturalistic perspective is prioritized over geometric preservation.
2026-02-06 15:09:58Tissot Indicatrix
Tissot Indicatrix is a classical method in cartography used to quantify and visualize distortions inherent in map projections. Developed by French mathematician Nicolas Auguste Tissot in the 19th century, it provides a precise geometric tool for analyzing how angles, areas, and shapes are deformed when transferring locations from the Earth's surface to a map. Rather than representing a projection itself, the indicatrix consists of plotting infinitesimal circles onto a projection grid to demonstrate how they become ellipses or other shapes under different projection transformations. This method enables an intuitive and scientific comparison of projection properties and remains foundational for evaluating projection suitability across mapping, geomatics, and geographic education.
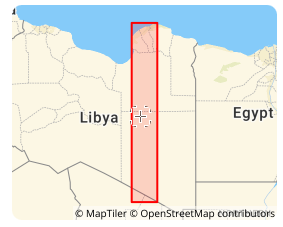
2026-02-06 14:53:50Libya Transverse Mercator coordinate system (EPSG:2062)
Libya Transverse Mercator coordinate system (EPSG:2062) is a projected coordinate reference system officially adopted by the State of Libya for national topographic mapping and cadastral surveying. Originally developed in the mid-20th century under Italian and later international geodetic influence, the system is based on the War Office ellipsoid and is historically tied to Libya’s national mapping infrastructure. While newer geocentric systems are increasingly used for GNSS applications, Libya TM remains critical for processing and maintaining historical geographic records, land administration documents, and foundational topographic series across the country.
2026-02-06 14:21:03Saudi Aramco Lambert coordinate system (EPSG:2329)
Saudi Aramco Lambert coordinate system (EPSG:2329) is a regional projected coordinate system historically developed and utilized by the Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco) for its internal exploration, mapping, and engineering operations. This proprietary system, based on a modified regional datum, was established to meet the company's specific needs for geodetic control and mapping across its expansive operating areas in eastern Saudi Arabia. While modern global systems are now prevalent, understanding this legacy system remains crucial for interpreting and integrating a vast archive of historical well data, seismic surveys, pipelines, and facility maps that form the foundation of Saudi Arabia's petroleum industry.
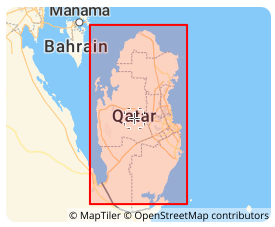
2026-02-06 14:16:25Qatar National Grid (Qatar National Grid 2009 | EPSG:28600)
Qatar National Grid (Qatar National Grid 2009 | EPSG:28600) is a projected coordinate system officially adopted by the State of Qatar for national surveying, mapping, and land administration. Established in 2009 through collaboration between Qatar’s Ministry of Municipality and Environment and international geodetic experts, this system provides a modern, GNSS-compatible framework optimized for Qatar’s compact territory and rapid urban development. It supports high-precision applications in construction, infrastructure, and cadastral management, serving as Qatar’s primary legal and technical coordinate reference.
2026-02-06 13:54:42Oblique Mercator Projection
Oblique Mercator Projection differs from the standard Mercator and Transverse Mercator projections by orienting the axis of the projection cylinder obliquely relative to the Earth's rotational axis and equator. This projection is designed to minimize distortion along a specific straight line or great circle, making it well-suited for high-precision representation of regions that are elongated in a diagonal direction. Notable examples of its use include mapping the Alaska Highway, long-distance pipelines, and geological structures that extend diagonally.
2026-01-31 14:37:48Patterson Cylindrical Projection
Patterson Cylindrical Projection is a pseudocylindrical projection proposed in 2014 by Tom Patterson, a cartographic editor at the National Geographic Society. Designed to emphasize visual balance, it aims to mitigate the excessive polar distortion seen in projections like Mercator and the vertical distortion characteristic of sinusoidal projections. As a result, it can depict the entire world with a gentle and natural impression. Although not an equal-area or conformal projection, it evenly distributes distortions in area, shape, and distance, making it suitable for modern world map representations.
2026-01-31 14:33:56
 Service
Service