Cube Projection
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Cube projection is a method of dividing the spherical surface of the Earth into six squares (each face of a cube), unfolding each square, and projecting it onto a flat surface. It is primarily used in 3D graphics, virtual reality (VR), spherical panoramas, and some GIS (geographic information systems), and is known as a method for efficiently mapping spherical data to 2D. Also known as a cube map, it has the advantage of being able to represent a three-dimensional environment.
Projection Basic
The cube projection is an approach that involves capturing images and performing calculations from six viewpoints (top, bottom, front, back, left, and right) centered on the Earth. It divides the Earth's surface into the six faces of a cube and treats each face as a square projection plane. This method has the following characteristics:
- Since each face is square, it is easy to handle as a texture, facilitating image processing and GPU optimization.
- Compared to other mapping methods such as the Mercator projection, it has significantly less distortion in polar regions.
- It can represent the entire surface with uniform resolution, making it particularly suitable for homogeneous processing of whole-sky or global data.
- As each face can be processed independently, it is also well-suited for parallel processing and streaming.
Pros
- Minimal distortion in polar regions: It largely avoids the stretching issues in polar areas that plague many map projection methods.
- Uniform resolution: It can maintain a consistent pixel density across the entire Earth's surface, making it suitable for image analysis and machine learning.
- Excellent for GPU optimization: It allows for high-speed processing on graphics cards as a cube map.
- High versatility: It can be utilized in various fields such as panoramic imaging, meteorological visualization, and space simulations.
Cons
- Seam processing due to division is required: Continuity processing (seamless integration) is necessary at the boundaries of the six faces.
- Relatively low compatibility with traditional GIS: Compared to conventional geographical projection methods, direct correspondence with latitude and longitude can be somewhat complex.
- Potentially low visibility: It may not always be suitable for intuitive map understanding (especially for general users).
Application Scenario
Cube projection is primarily used for spherical panoramic images and environmental mapping in virtual spaces, and is essential for background processing in game engines and VR spaces that require real-time rendering. It is also effective in fields that require highly accurate and uniform processing of data, including polar regions, such as global weather simulations and visualization of ocean and atmospheric data. Its applications are also expanding to equal-resolution processing of satellite images and global WebGIS display.
Example
1. A cube map projection can be collapsed into a cube.
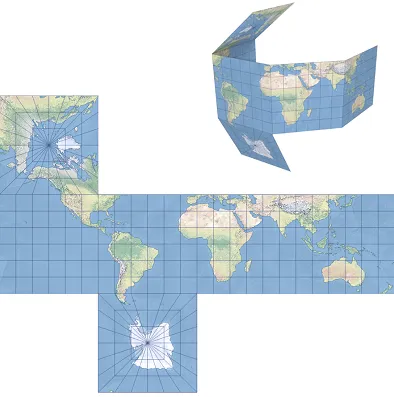
2. Development of a quadrilateral spherocubic projection on the Earth model.

Related GIS Projections
Transverse Mercator Projection
Longitude / Latitude Projection

 Service
Service
