Gaia-CRF3 (Gaia Celestial Reference Frame 3)
Dec 29,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Gaia-CRF3 (Gaia Celestial Reference Frame 3) is the latest generation of celestial reference frame constructed by the European Space Agency's (ESA) Gaia satellite mission. It primarily uses ultra-distant celestial objects such as distant galaxies and quasars as reference points, providing a highly accurate spatial coordinate reference in space that is unaffected by Earth's motion or rotation. Gaia-CRF3 serves as a foundation for position determination in astronomy and space geodesy, complementing and enhancing the previous ICRF (International Celestial Reference Frame).
Projection Basic
Gaia-CRF3 is not a file format but a celestial reference system composed of observational data and mathematical definitions, structured by the following elements:
- Reference Celestial Catalog: Includes hundreds of thousands of quasars and active galactic nuclei (AGN), serving as effectively fixed reference points on the celestial sphere.
- Celestial Coordinate Definition: Adopts a three-dimensional angular coordinate system based on right ascension (RA) and declination (Dec), in accordance with the International Astronomical Union (IAU).
- Observational Dataset: Constructed using high-precision astrometric data (position, annual parallax, and proper motion) obtained from Gaia satellite observations.
- Integration with Time Reference: Celestial positions are tied to specific reference epochs, enabling precise coordinate management that accounts for temporal changes.
- Consistency with ICRS: Maintains high alignment with the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS), allowing interoperability with terrestrial geodetic systems and VLBI observations.
Pros
- Exceptionally High Positional Accuracy: Achieves microarcsecond-level precision, significantly surpassing the accuracy of previous celestial reference frames.
- Stability Unaffected by Earth's Motion: Uses distant galaxies as reference points, making it immune to Earth's rotation, orbital motion, or crustal movements.
- High Compatibility with ICRF: Designed to align with the radio astronomy-based ICRF, providing a unified spatial coordinate framework across wavelengths.
- Contribution to Space Geodesy: Facilitates the construction of an integrated geodetic framework linking Earth and space by combining with terrestrial reference frames like ITRF.
- Future Scalability: Continuous improvement in accuracy is possible through additional data releases from the Gaia mission.
Cons
- Specialized Usage: Primarily intended for astronomy and astrophysics, with no direct application in general GIS or mapping.
- High Complexity in Data Processing: Requires consideration of relativistic corrections and time dependencies, demanding advanced expertise.
- Challenges in Direct Correspondence with Terrestrial Coordinate Systems: Lacks direct mapping to geographic coordinate systems like WGS84, necessitating geodetic models for conversion.
- Celestial-Dependent Observation Errors: Positional accuracy may vary depending on the brightness or structure of reference objects.
- Unsuitable for Real-Time Use: Functions as a static reference frame, making it inadequate for real-time positioning or navigation purposes.
Application Scenario
Gaia-CRF3 serves as a fundamental position reference in astronomy for precise measurements of star and galaxy positions, analysis of celestial motions, and unification of coordinates on a cosmic scale. In particular, it provides the foundation for multi-wavelength astronomical research by integrating observational results from radio and optical astronomy into a common reference frame. In the field of space geodesy, it works in conjunction with the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) to establish high-precision linkages between Earth and space positions. It is an essential reference coordinate system for advanced space science research, including attitude determination for deep-space probes, celestial navigation, and verification of fundamental physical constants.
Example
1. Example of (Gaia-CRF3) characteristics.
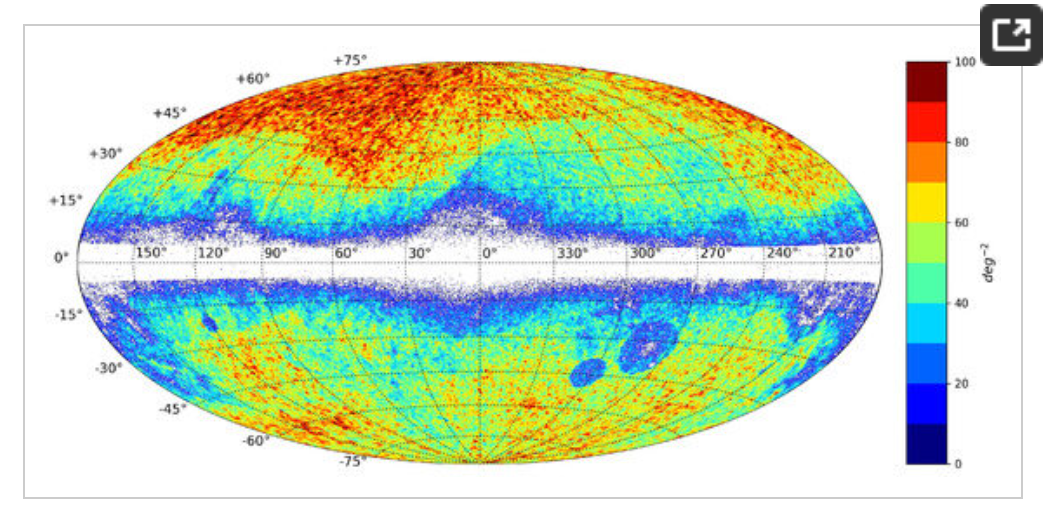
2. Example of (Gaia-CRF3) characteristics.
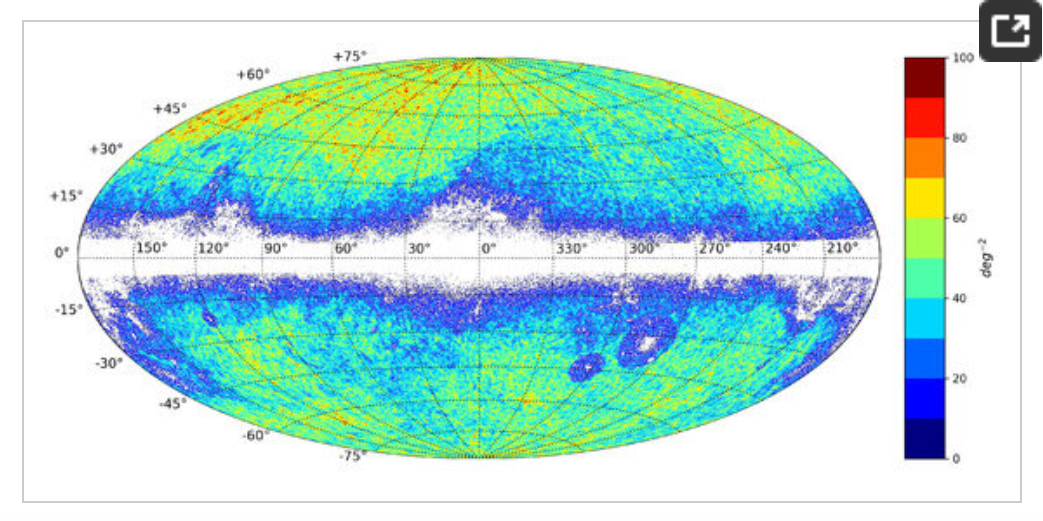
Related GIS Projections
Vertical Near-side Perspective Projection
Two-point Equidistant Projection

 Service
Service
