Patterson Projection
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Patterson projection is a compromise cylindrical map projection designed by Tom Patterson. Its structure of equally spaced meridians and symmetrical parallels achieves low distortion in the equatorial region while optimizing the shape of high-latitude regions (superior to the Miller projection). Although it is a non-equal-area projection and only supports spherical models, its visual balance and compatibility with mainstream GIS platforms such as ArcGIS make it widely used in scenarios that do not require precise area calculations, such as education and popular science, time zone display, and thematic mapping of areas around the equator.
Projection Basic
- Geometric Perspective
- Projection Surface Type: Uses a plane, cylinder, or cone as the projection surface, projecting features of the Earth's surface onto the plane through raycasting.
- Distortion Control: Controls the degree of distortion of lengths, areas, and angles by adjusting the projection center position, angle, or distance. For example, the Stereographic projection preserves angles but distorts areas; the Mercator projection maintains orientation but significantly exaggerates areas at high latitudes.
- Mathematical Analysis
- Equation Definition: Directly describes the conversion relationship between longitude and latitude and plane coordinates through mathematical formulas, such as the longitude and latitude equations in the Patterson projection.
- Parameter Optimization: Balances distortion in different regions by adjusting parameters such as the scale factor and standard parallels. For example, the UTM coordinate system uses a scale factor (0.9996) to reduce distortion near the central meridian.
Pros
- Minimal distortion at high latitudes: More accurately represents polar regions (e.g., Greenland) with less shape distortion compared to the Miller projection.
- Visually balanced: Proportional map layout avoids extreme stretching, making it suitable for general-purpose use in education and media.
- Time-zone friendly: Equal spacing of meridians ensures minimal distortion of time zones at high latitudes, ideal for global time-zone displays or longitude-related phenomena.
- User-friendly: Compatible with mainstream GIS software (e.g., ArcGIS), enabling easy and quick map production.
Cons
- Inaccurate area representation: Fails to preserve true area proportions, potentially exaggerating or shrinking high-latitude regions (e.g., Greenland still appears oversized).
- Limited to spherical models: Only applicable to spherical Earth models; requires approximation for ellipsoidal models, reducing accuracy for high-precision surveying.
- Residual polar distortion: While optimized, some shape distortion remains in polar areas, making it unsuitable for specialized polar maps (e.g., Antarctic expedition routes).
- Compromised design: Balances shape, area, and distance distortions at the expense of optimal performance in any single category, necessitating specialized projections for strict requirements.
Application Scenario
The Patterson projection is suitable for general world map presentations in education and popular science, global views in news media that require a balance between regional shape and overall readability, time zone divisions and other scenarios that require high requirements for the shape of the polar regions, and thematic maps centered on continents near the equator (such as South America and Africa). However, it is not suitable for geographic analysis tasks that require precise area calculations.
Example
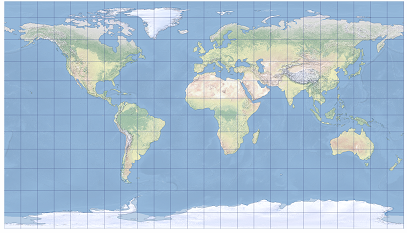
1. The Patterson cylindrical map projection is shown centered on Greenwich.
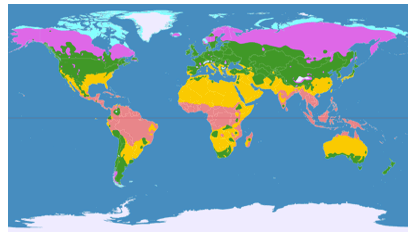
2. Climatic Map for the Patterson projection.
Related GIS Projections
Transverse Mercator Projection
Longitude / Latitude Projection

 Service
Service
