QGIS Cloud
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
QGIS Cloud is a cloud-based geographic information platform based on QGIS. It allows users to quickly publish desktop GIS projects as web maps using a plugin, enabling server-free spatial data sharing. It provides a personalized spatial data infrastructure (SDI) and supports PostgreSQL/PostGIS database management. It is available in two service models: a free (public access) version and a Pro (access control) version. This platform simplifies the map publishing process, allowing users to deploy maps to the cloud by simply installing a plugin in QGIS Desktop.

File Structure
- Project files: Use XML format to store QGIS session state, including settings for 28 aspects, including layer configuration, coordinate system, print layout, and symbology styles. These files can be packaged in *.qgz format, integrating all associated data and style configurations.
- Data Storage Structure: Vector data is managed in a PostgreSQL/PostGIS database, supporting spatial indexes and attribute table joins. Raster data uses a pyramid structure for accelerated display, supporting cloud-based tile loading of COG (Cloud Optimized GeoTIFF) format. Point cloud data is compatible with the E57 format and supports dynamic thinning and classification rendering.
- Cloud-specific components: The QGIS Cloud plugin enables seamless publishing of local projects to the cloud, including a map rendering engine and OGC service interfaces. A personal PostgreSQL database is a dedicated cloud database for each user, supporting SSL encryption and spatial data management.
- Metadata and Configuration: This includes metadata such as CRS definitions (such as WGS84 EPSG:4326), default style libraries, and plugin configurations. Data source connections and symbology rules can be defined using XML files.
Pros
- Open Source and Free: QGIS Cloud is based on an open source architecture and requires no licensing fees, making it ideal for individual users and small teams on a budget.
- Seamless Integration: The QGIS Cloud plugin allows for seamless integration between local project files and cloud databases, enabling one-click publishing and sharing.
- Multi-Format Support: Compatible with over 70 vector formats (such as Shapefile and GeoJSON) and raster data (such as COG), and supports PostgreSQL/PostGIS spatial database management.
- Cross-Platform: Supports Windows, macOS, and Linux, and the cloud service requires no in-house server infrastructure.
- Plugin Ecosystem: A rich library of plugins (such as MetaSearch and QField Sync) extends functionality, including data download, synchronization, and 3D analysis.
Cons
- Performance Limitations: Rendering may be slow when processing large-scale raster data (such as global DEMs), requiring data segmentation or GPU acceleration.
- Learning Curve: The interface is densely populated, requiring a long time for beginners to master advanced operations like symbolization and spatial analysis.
- Lack of Enterprise Features: Compared to ArcGIS Pro, it lacks advanced 3D editing tools (such as skyline analysis) and a comprehensive permissions management system.
- Community Support Limitations: Professional questions are answered by the developer community, and response times may be slower than those for commercial software.
Application Scenario
As an open source geographic information system cloud platform, QGIS Cloud's application scenarios mainly cover cloud storage, sharing, and collaborative analysis of geographic data. Users can use plug-ins to publish local QGIS projects as online maps with one click, and support sharing with team members or the public through links without the need to build their own server infrastructure. Its personal PostgreSQL database function is suitable for users who need cloud-based spatial data management, while the QField Sync plug-in enables data synchronization between desktop and mobile terminals to meet field collection needs. Educational institutions and non-profit organizations often use its free features for GIS teaching and project development, such as creating administrative division visualizations by overlaying OSM or Google Maps as base maps. In addition, the platform supports multi-person collaborative editing and is suitable for team work scenarios that require real-time geographic data updates.
Example
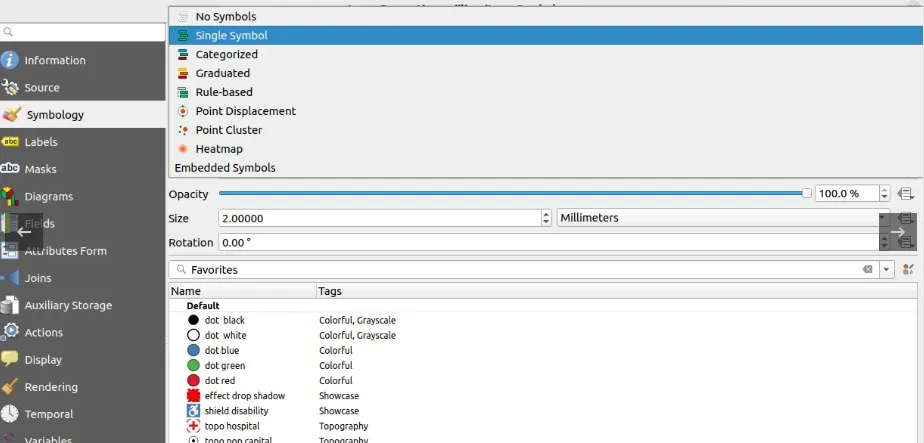
1. Feature rendering methods provided by QGIS.
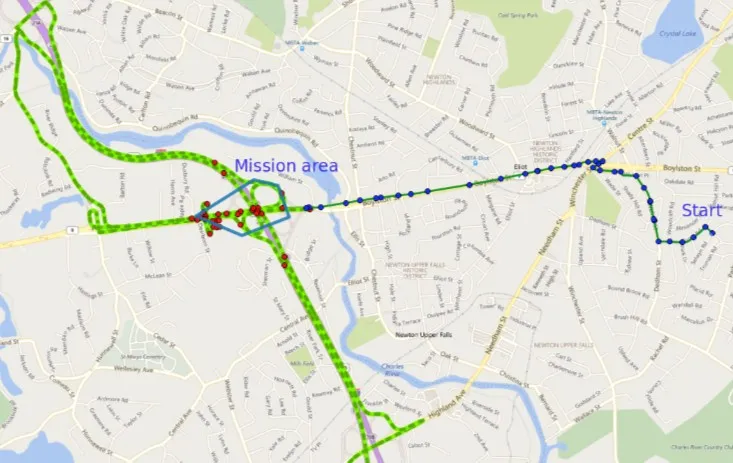
2. QGIS loads the online map.
File Opening Mode
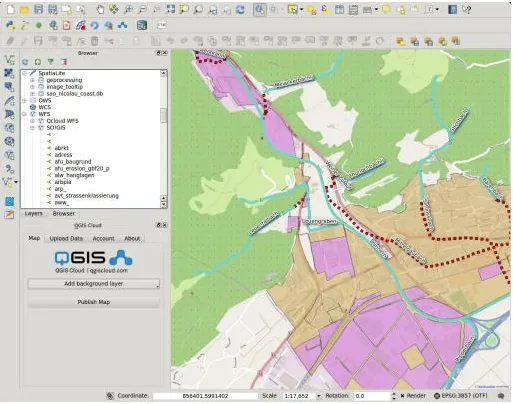
1. Create a map with your own data in QGIS Cloud.

 Service
Service
