NITF (National Imagery Transmission Format)
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
NITF (National Imagery Transmission Format) is a specialized imagery data format developed by the United States Department of Defense, primarily for the storage and transmission of high-definition grayscale and color imagery for military and intelligence purposes. This format supports multiple compression methods (such as JPEG and JPEG2000) and integrates text, graphics, and metadata into a single file, conforming to the ISO/IEC 15444-1 standard. Features include high-precision geographic coordinate support (via IGELO or RPC metadata) and cross-platform compatibility (parsable with tools such as GDAL), making it widely used for satellite imagery, aerial photography, and government data exchange.
File Structure
The NITF (National Imagery Transmission Format) file structure consists of the following core components:
- File header: Contains metadata such as file identifier, version information, and file type, identifying the overall properties and compatibility of the NITF file.
- Image segment: Stores the actual image data, supporting various compression formats (such as JPEG and JPEG2000) as well as uncompressed data, and may contain georeferencing information (such as IGEOLO and RPC metadata).
- Ancillary data segment: Contains additional information such as text, graphics, and symbols, supplementing the image content (such as CIB/CADRG framework data for RPF products).
- Extension segment: Such as BLOCKA instances or GeoSDE TREs, provides higher-precision coordinates or metadata extensions.
- File trailer: Marks the end of the file and may contain checksum information or version control data.
Pros
- Standardization and Compatibility: NITF is an international standard format for military and remote sensing applications, supporting cross-system data exchange and particularly suitable for government, defense, and geographic information system (GIS) applications.
- Multiple Data Type Support: It can store images, text, graphics, geographic coordinates (such as IGEOLO and RPC metadata), and sensor information, supporting multiple layers.
- High Compression Efficiency: It supports compression algorithms such as JPEG2000, significantly reducing file size while maintaining image quality, making it suitable for remote sensing and large-scale image transmission.
- Rich Metadata: It contains complete image description information (such as capture time, device parameters, and georeferencing), facilitating data management and analysis.
Cons
- Large file size: Uncompressed or high-resolution NITF files can take up a significant amount of storage space, especially for 3D sequences or multi-band data.
- High parsing complexity: Parsing requires specialized libraries (such as GDAL or MATLAB's NITF toolkit), which have a high development threshold and are difficult for ordinary users to directly process.
- Low universality: Primarily used in military and remote sensing fields, support in civilian software (such as Photoshop) is limited, requiring format conversion for universal editing.
- Limited transmission efficiency: Large files transfer slowly in low-bandwidth environments, potentially impacting scenarios requiring high real-time performance.
Application Scenario
NITF (National Imagery Transmission Format) is primarily used in military, remote sensing, and geographic information systems (GIS) applications. It supports the storage and transmission of high-resolution satellite imagery and drone reconnaissance data, integrating geographic coordinates and metadata to facilitate spatial analysis. Its standardized nature makes it the preferred format for sharing imagery data among defense and intelligence agencies, and it also plays a key role in map production, environmental monitoring, and disaster assessment. NITF also has applications in smart city development and agricultural resource management, such as optimizing land use and analyzing crop growth through GIS technology.
Example
- NITF dataset browser.
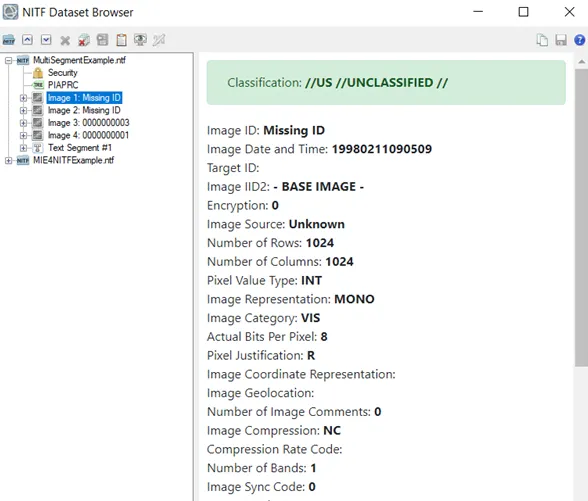
File Opening Mode
- US Army NGA .ntf image format.
Related GIS files
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Imagery_Transmission_Format
- https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/help/data/nitf/introduction-to-nitf-data.htm
- https://gdal.org/en/stable/drivers/raster/nitf.html

 Service
Service
