Azimuthal Equidistant Projection
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Azimuthal equidistant projection is a map projection that is drawn to accurately maintain direction and distance from a single point (reference point) on the Earth. Its greatest feature is that the straight-line distance and azimuth angle from the center point to all other points are accurately represented on the map. It is often used in applications where accuracy of direction and distance is important, such as air navigation and communications.
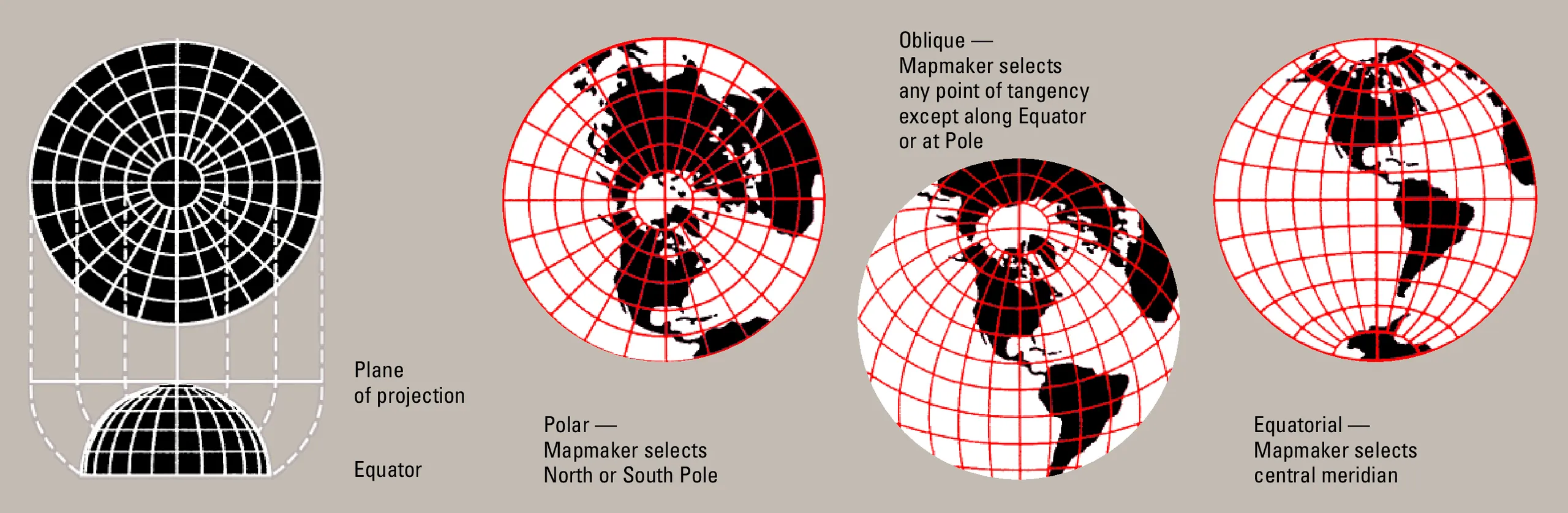
Projection Basic
This projection develops the Earth as a "plane" seen from the center point, so it radiates out from the center. The parallels are drawn as concentric circles, and the meridians are drawn as straight lines radiating from the center. The further away from the center of the map, the more distorted the shape and area become, but the straight-line distance and direction from the center are always accurate.
Pros
- Accurate distance from the center: It is possible to measure the distance from a reference point to any other point directly on the map.
- Orientation is maintained: The orientation from the center point to other points is correct, making it suitable for navigation and radar analysis.
- The entire Earth can be shown on a single image: When the pole is used as the center, it is possible to create a projection map that can show the entire Earth on a single image.
Cons
- Shapes become more distorted the further away from the center: The closer you get to the edge of the map, the more severe the distortion of area and shape.
- It becomes difficult to see over a wide area: When used as a world map, visibility of surrounding areas tends to be poor.
- The appearance changes depending on the reference point: Choosing a different center point can greatly change the display of the same area.
Application Scenario
The Azimuthal Equidistant Projection is used in all situations where distance and direction from a certain point are important, such as route planning for air navigation, coverage area maps for shortwave radio communication, analysis of the epicenter distance of an earthquake, or visualization of the geographical influence range from a specific point. Typical examples include access maps to the world centered on Tokyo, and influence maps from a reference point for disaster response.
Example
1. A conceptual diagram of the azimuthal equidistant projection.
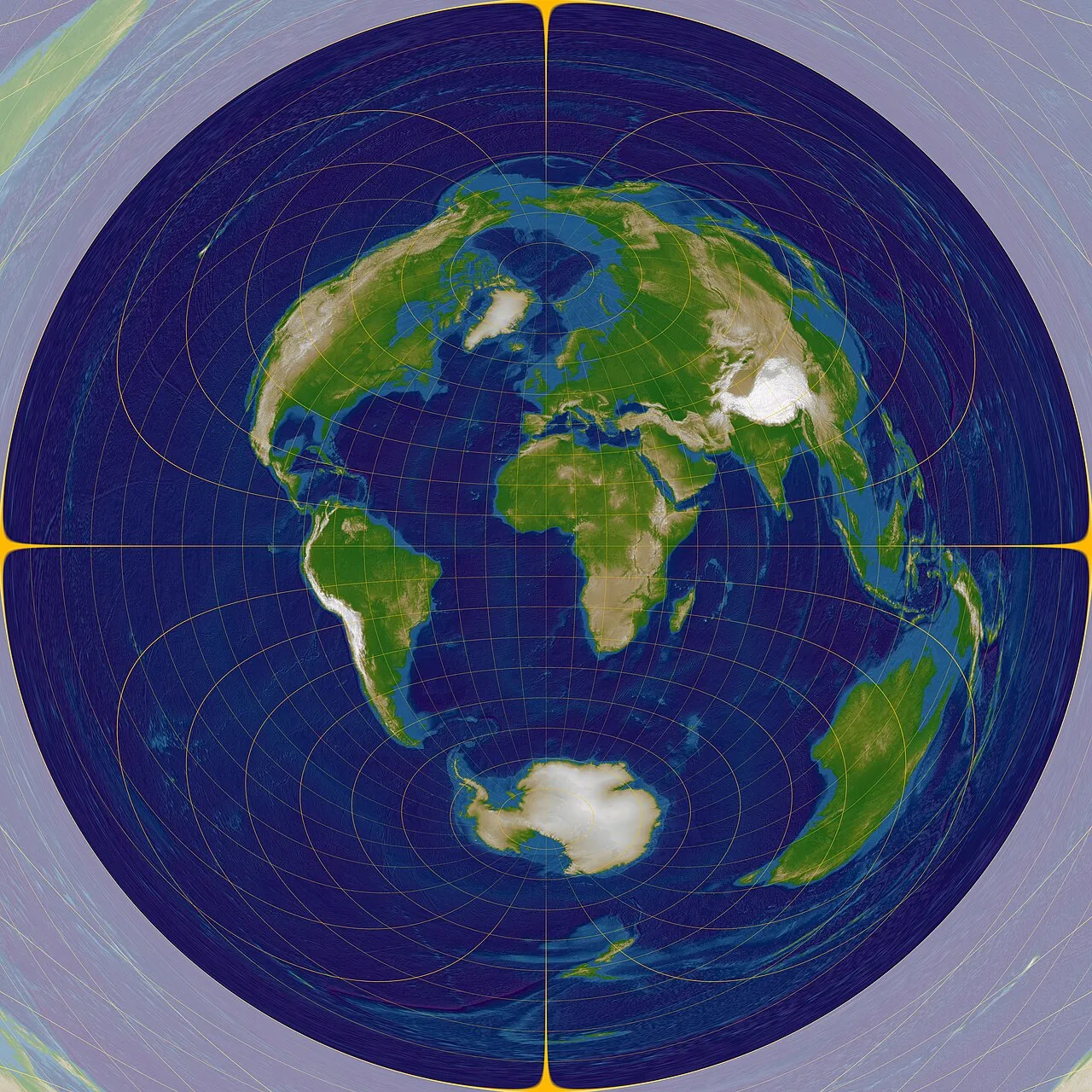
2. An azimuthal equidistant projection centered at 0 degrees latitude and longitude.
Related GIS Projections
Transverse Mercator Projection
Longitude / Latitude Projection

 Service
Service
