Irish Transverse Mercator
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Irish Transverse Mercator (ITM) is a transverse Mercator projection coordinate system designed specifically for Ireland, using the ETRS89 ellipsoid as the reference. The central meridian of its projection is 8 degrees west longitude, and the geographic coordinates of the Irish region are converted into plane coordinates through the horizontal axis isometric cylindrical projection method to reduce deformation and meet national surveying and mapping needs. This coordinate system is the primary projection system for official maps and geospatial data of Ireland.
Coordinate System Composition
1. Projection method: Transverse Mercator projection is used, with the central meridian at 8 degrees west longitude. The geographic coordinates of the Irish region are converted to plane coordinates by tangency between the cylinder and the ellipsoid.
2. Reference ellipsoid: Based on ETRS89 ellipsoid, ensuring consistency with European geodetic datum.
3. Coordinate unit: Cartesian coordinates on a plane are measured in meters (m) for easy distance and area calculations.
4. Deformation control: Reduce length and area deformation through central meridian projection, suitable for precise mapping in mid latitude regions of Ireland.
Pros
1. Isometric feature: Maintain the shape and angle of the local area unchanged, suitable for precise measurement and mapping needs.
2. Central meridian optimization: centered on the mainland of Ireland (longitude 8 ° W), minimizing projection distortion, especially suitable for longer north-south regions of Ireland.
3. Unified benchmark: using ETRS89 ellipsoid, consistent with the European continental coordinate system, facilitating cross-border data integration.
Cons
1. Area deformation: When moving away from the central meridian, the area deformation significantly increases and is not suitable for large-scale area analysis.
2. Length distortion: The ratio of length in the east-west direction becomes distorted as the distance from the central meridian increases, which needs to be alleviated by zoning or limiting the range of use.
3. Computational complexity: It is necessary to consider the conversion between ellipsoid parameters and projection parameters, which poses a high threshold for non professional users.
Application Scenario
The Irish Trans Mercator (ITM) coordinate system is mainly used for surveying, engineering construction, and geographic information system (GIS) applications in Ireland. Its isometric characteristics and optimized design of the central meridian ensure the accuracy of domestic maps and spatial data. This coordinate system is also applicable for topographic mapping of Northern Ireland and forms regional complementarity with the UK OSGB coordinate system. In addition, ITM has broad practicality in fields such as land management, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure planning that require high-precision planar coordinates.
Example
1. EPSG: 2157 Irish projection coordinate system.
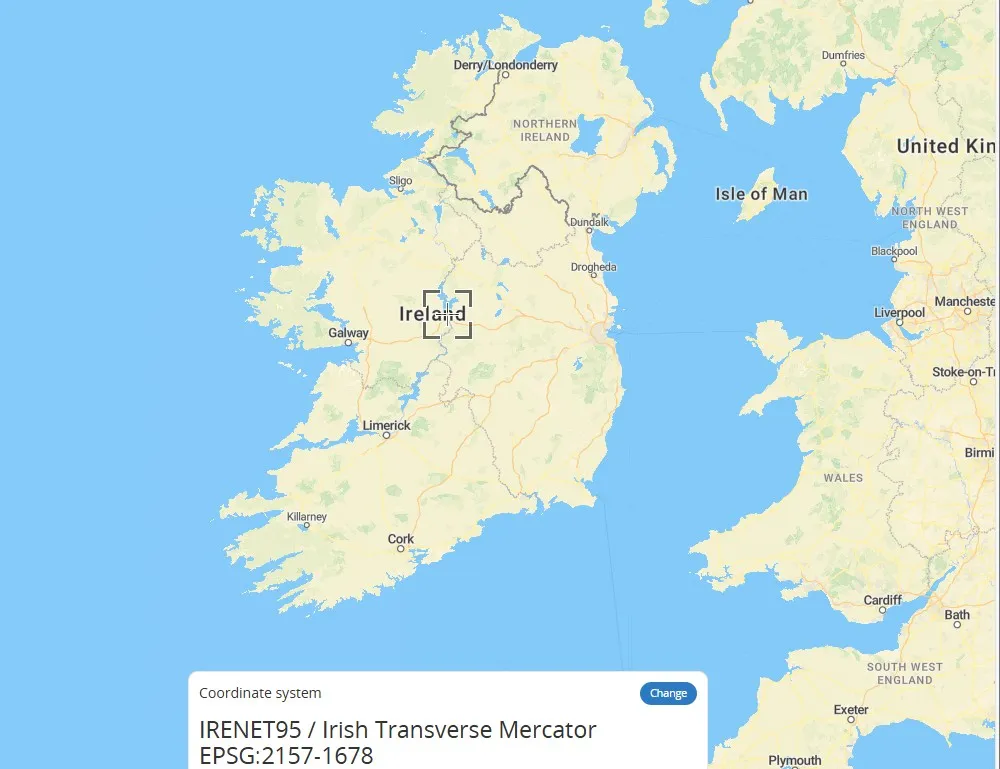
2. The Irish transverse Mercator.
Related GIS Coordinate Systems
References
- https://epsg.io/map#srs=2157-1678&x=603320.631691&y=745329.377778&z=7&layer=streets
- https://www.osgeo.cn/proj/operations/projections/tmerc.html

 Service
Service
