Times Projection
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Times projection is a compromise pseudocylindrical map projection developed by John Moir in 1965 for the British cartographic company Bartholomew Ltd. It is based on a modified Gall stereographic projection, but with meridians as curved lines rather than straight lines.
Projection Basic
- Meridian and Latitude Characteristics:
- The equator and central meridian are projected as straight lines.
- Other meridians are equally spaced sinusoidal curves.
- Latitudes and both poles are straight lines.
- Distortion Characteristics:
- The Times projection is neither conformal nor equal-area; shapes, areas, distances, directions, and angles are generally distorted.
- The projection is correctly scaled along the standard parallels of 45° north and south.
- Distortion increases away from the standard parallels and is most severe in polar regions.
- Distortion values are symmetric about the equator and the central meridian.
Pros
- Good Visual Balance: The Times projection, with its curved meridians, achieves a relatively balanced visual presentation of mid-latitude regions, avoiding extreme distortion that would affect the overall aesthetics of the map. It is suitable for scenarios requiring a balance between visual quality and the communication of geographic information.
- Distortion in Mid-Latitudes is Controllable: Around the standard parallels of 45° North and South, the Times projection exhibits minimal scale and shape distortion, accurately reflecting the geographic features of mid-latitude regions. It is suitable for maps depicting densely populated or economically active regions, such as temperate and subtropical zones.
- Relatively Easy to Create: As a pseudocylindrical projection, the Times projection is relatively simple to calculate and render, requiring no complex mathematical models or high-precision calculations, thus lowering the barrier to entry and the cost of map production.
- Good Compatibility: The Times projection is compatible with a variety of Geographic Information System (GIS) software, such as ArcGIS Pro 1.0 and above and ArcGIS Desktop 8.1.1 and above, making it easy to use in digital map production.
Cons
- Severe distortion in polar regions: The Times projection significantly distorts shapes, areas, distances, and directions in polar regions (near the poles), resulting in inaccurate representation of polar geographical features. Therefore, it is not suitable for polar exploration, scientific research, or scenarios requiring high-precision polar data.
- Area distortion increases with latitude: Area distortion increases from the standard parallels toward the poles, with high-latitude areas being significantly exaggerated or reduced. This can mislead the understanding of geographic spatial relationships and is particularly unsuitable for scenarios requiring precise area measurements (such as resource allocation and ecological protection planning).
- Limited directional accuracy: The Times projection's directional representation is not globally accurate, especially in areas far from the standard parallels. Directional deviations can affect navigation or path planning accuracy.
- Spherical models only: The Times projection is designed for spherical models. When applied to ellipsoidal models (e.g., the true shape of the Earth), it uses the average of the semi-major and semi-minor axes for approximation, which may result in some loss of accuracy.
- Unsuitable for high-precision scenarios: Due to its distortion characteristics, the Times projection cannot meet the needs of scenarios requiring high-precision geographic information, such as land surveying, engineering planning, and military operations.
Application Scenario
The Times projection is suitable for general world maps that do not require precise area measurements and are mainly for visual presentation. It is particularly well suited for displaying mid-latitude regions, but should be avoided for polar regions or high-precision geographic analysis scenes.
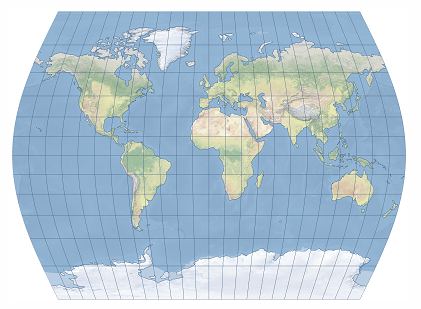
Example
1. The Times projection is shown centered on Greenwich.
Related GIS Projections
Transverse Mercator Projection
Longitude / Latitude Projection

 Service
Service
