SAD69 (South American Datum 1969 | EPSG:4618)
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
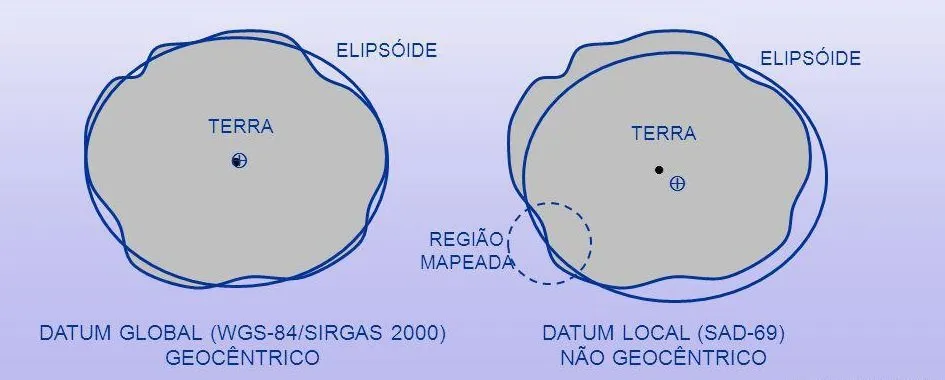
SAD69 coordinate system is the abbreviation of South American Datum 1969, which is a geodetic reference system widely used in South America. It is based on the Krasovsky ellipsoid and established through the astronomical geodetic network data of Brazil, Argentina and other countries. It is mainly used for topographic mapping and geographic information applications in South American countries. This coordinate system has local deformation due to regional gravity field differences and is gradually being replaced by more accurate modern datums such as SIRGAS2000.
Coordinate System Composition
The SAD69 coordinate system primarily consists of three components: the reference ellipsoid, the geodetic datum, and the coordinate system:
- Reference Ellipsoid: The SAD69 coordinate system adopts the Krasovsky ellipsoid as its mathematical foundation. This ellipsoid is defined by specific parameters, such as the semi-major axis and flattening, which are used to approximate the shape of the Earth.
- Geodetic Datum: The geodetic datum serves as the reference that connects the reference ellipsoid to the actual shape of the Earth. In the SAD69 coordinate system, the positioning and orientation of the reference ellipsoid in the South American region are determined using observed data from astronomical-geodetic networks, thereby establishing a geodetic datum that best fits the local geoid in this area.
- Coordinate System: Based on the reference ellipsoid and geodetic datum, the SAD69 coordinate system establishes a framework for describing geographic locations in South America. This system typically employs either a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system or a geodetic coordinate system to represent the positions of ground points. In the three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, the origin is located at the center of the reference ellipsoid, the Z-axis points towards a specific direction such as the Conventional International Origin (CIO), and the X-axis and Y-axis form a right-handed coordinate system with the Z-axis.
Pros
- Regional Applicability: The SAD69 coordinate system, established based on astronomical-geodetic network data from South America, exhibits good fit with the geoid in this region, meeting the needs of South American countries for topographic mapping and geographic information applications.
- Historical Continuity: During its initial establishment, the SAD69 coordinate system provided a unified reference for geospatial data across South America, enabling the integration and analysis of data from different periods and sources within the same framework, thereby laying the foundation for regional geographical research and development.
Cons
- Ellipsoid Parameter Errors: The parameters of the Krasovsky ellipsoid contain errors compared to modern, highly precise ellipsoid parameters, such as an approximately 109-meter discrepancy in the semi-major axis. These errors lead to inaccuracies in coordinate calculations, affecting the precision of measurements and positioning.
- Non-Conformity with the Geoid: There exists a systematic tilt between the reference ellipsoid surface and the geoid in South America, with the maximum geoid separation reaching up to 60 meters in the eastern region. This non-conformity impacts the accuracy of elevation calculations, posing challenges for topographic mapping and geographic information applications.
- Inconsistency Between Geometric and Physical Geodetic Reference Surfaces: When processing gravity data, the Helmert normal gravity formula used is inconsistent with the Krasovsky ellipsoid, resulting in a lack of uniformity between the reference surfaces for geometric and physical geodetic applications. This increases the complexity of practical work.
Application Scenario
The SAD69 coordinate system is mainly used in the fields of geographic surveying and mapping, land management and infrastructure construction in South America. It provides a unified geodetic benchmark for South American countries and is suitable for practical needs such as topographic mapping, boundary demarcation, road and water conservancy project planning. In addition, the coordinate system also played an important role in early geographic information systems (GIS) and resource surveys, providing a basic framework for the integration and analysis of regional geographic data.
Example
1. SAD69 has a geocentric orientation, meaning that its origin and orientation are on the Earth's surface.
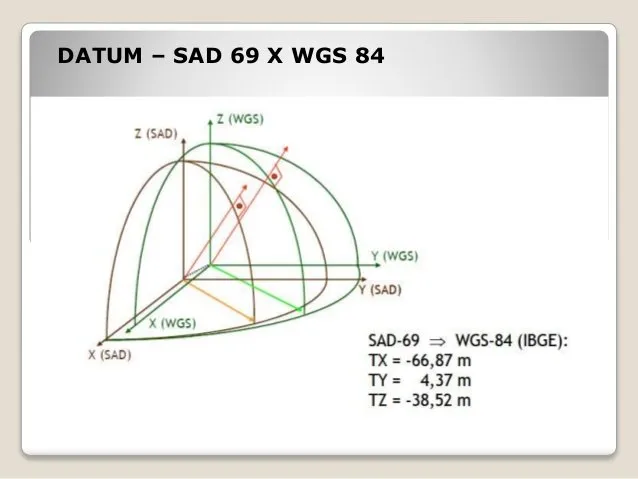
2. South American Datum (SAD69).

 Service
Service
