Gnomonic Projection
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Gnomonic projection is a method in which a straight line is drawn from the center of the Earth to any point on the Earth's surface, and projected to the point where it intersects with a plane tangent to the Earth. This is a type of perspective projection (central projection), and has the characteristic that "great circle routes (shortest routes)" on the Earth are represented as straight lines after projection. For this reason, it is very useful when you want to show the shortest distance with a straight line.
Projection Basic
The gnomonic projection is a perspective projection method that projects points on the Earth's surface onto a tangent plane, with the center of the Earth as the projection point. This projection has the characteristic that great circles (the shortest route on the Earth) are always drawn as straight lines, and plays an important role in designing sea routes and air routes. However, it has large distortions of area, shape, and direction, and the range that can be expressed is limited, so it is a projection specialized for specific purposes.
Pros
- Great circle routes are drawn as straight lines, making it useful for understanding the shortest routes for air routes and sea voyages.
- Mathematically, it is a very clear projection method, and its geometric properties are easy to understand.
- It is suitable for visualizing three-dimensional perspective effects from the center of the Earth.
Cons
- Area, distance, and shape are all distorted, and distortion increases rapidly as you move away from the projection center.
- It is impossible to represent the entire Earth, so it is not suitable for representing a wide area on a single map.
- It has a narrow range of practical use and can only be used for limited, localized visualization.
Application Scenario
Gnomonic projections are used in fields such as navigation and aviation, where a visual understanding of the shortest distance (great circle course) is required. For example, when an airline plans a route for a long-distance flight, they may use the Gnomonic Projection to visualize the shortest route drawn in a straight line, and then convert it into a route chart or similar. They are also used as teaching materials to explain the principles of earth projection in mathematics and geography education.
Example
1. Explanation of the gnomonic projection.
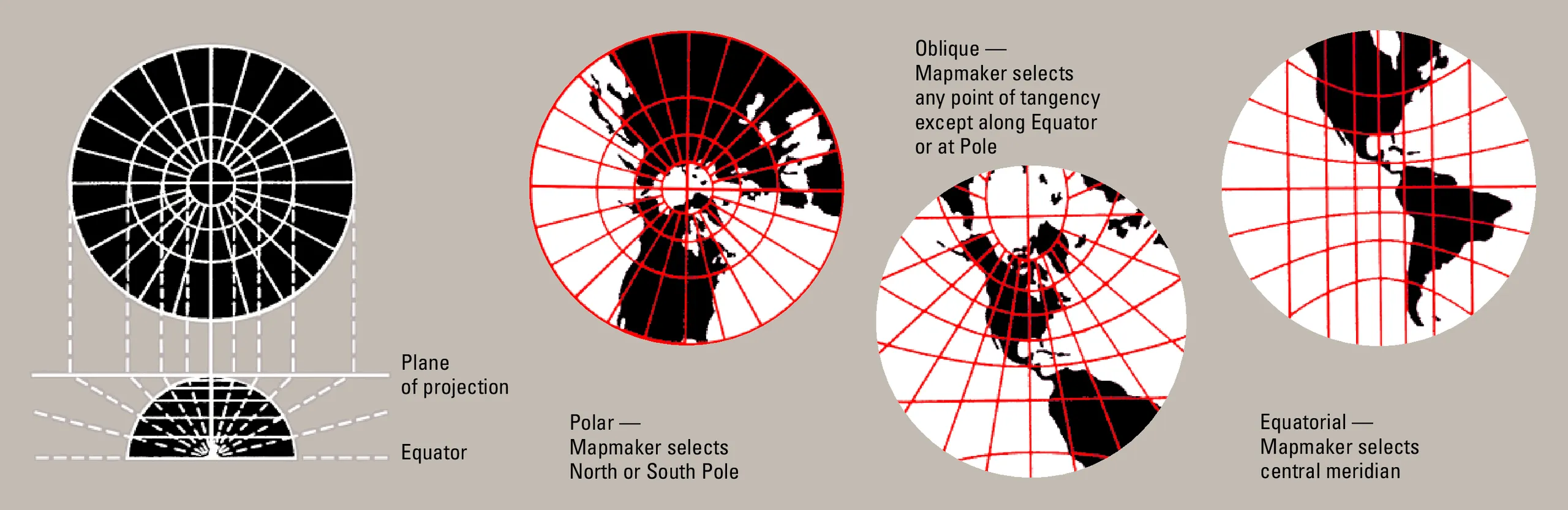
2. Gnomonic projection centered on the North Pole.

Related GIS Projections
Transverse Mercator Projection
Longitude / Latitude Projection

 Service
Service
