LandXML (Civil Engineering Data Exchange Format)
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
LandXML is an XML-based civil engineering data exchange format primarily used for sharing infrastructure design data such as roads, terrain, and land parcels between different CAD platforms. It uses standardized data structures to transfer geometric information (such as surfaces and COGO points) and attribute data between software like Autodesk Civil 3D. It supports specialized parameters such as northing/easting/elevation coordinate systems and station number disconnection. This format is particularly suitable for terrain processing and survey data import, effectively reducing model conversion time and maintaining data integrity.

File Structure
- Root element: Serves as the root container for the entire file, containing all project data.
- Metadata module: Describes basic project properties, such as name, number, and coordinate system.
- Terrain data module: Stores terrain surface data, including elevation points, contour lines, and triangulated networks.
- Road design module: Describes the geometric information of linear projects such as roads and pipelines.
- Pipeline system module: Stores drainage, water supply, and other pipeline network data.
- Extension and customization module: Supports the extension of project-specific data.
Pros
- Cross-platform and software compatibility: As an open, non-proprietary format, LandXML is independent of specific software and supports data exchange across platforms such as Autodesk Civil 3D and Tuxin Cloud GIS.
- Standardized data structure: Predefined tags (such as <Surfaces> and <Alignments>) standardize data organization, ensuring structured storage of engineering information such as terrain, roads, and pipelines.
- Long-term data archiving and reuse: LandXML provides a data format suitable for long-term storage, supporting data transfer throughout the entire lifecycle, from design to construction and maintenance.
- Support for complex engineering objects: This includes survey data, alignments, corridors, pipelines, and other information, meeting the needs of the GIS and road sectors.
Cons
- Limited semantic expression capabilities: The XML format alone cannot solve the problem of integrating heterogeneous data across different locations, and requires the use of other technologies (such as Schema extensions) to achieve cross-platform interoperability.
- Data redundancy and parsing efficiency: Compared to lightweight formats like JSON, XML's tag structure can lead to data redundancy, affecting the efficiency of large-scale data transmission and processing.
- Scalability and maintenance costs: While custom extensions are supported, ensuring that the extension tags conform to the Schema specification may cause compatibility issues.
- Coordinate system and unit processing relies on external definitions: Coordinate system information must be explicitly specified through the <CRS> tag or EPSG number. Failure to define the coordinate system may lead to data misalignment.
Application Scenario
LandXML is widely used in civil engineering for cross-platform data collaboration, such as exporting road design data from Civil 3D to other BIM software for collaborative design, or integrating topographic surveys, pipe network layouts, and construction records through standardized formats. This supports information sharing throughout the entire lifecycle, from planning to operation and maintenance, while providing a traceable open data carrier for long-term engineering archive storage.
Example
- LandXML to PLY.
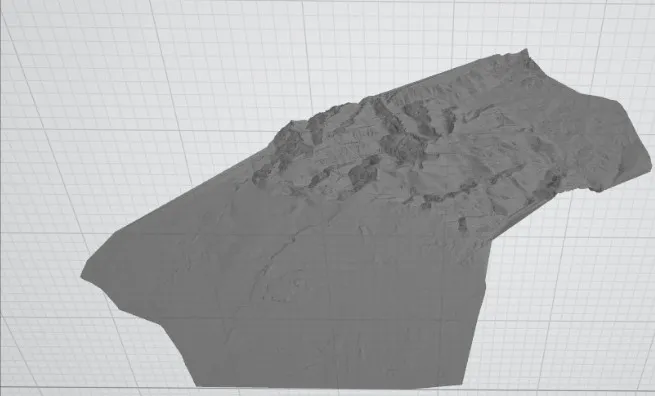
File Opening Mode
- Import LandXML.
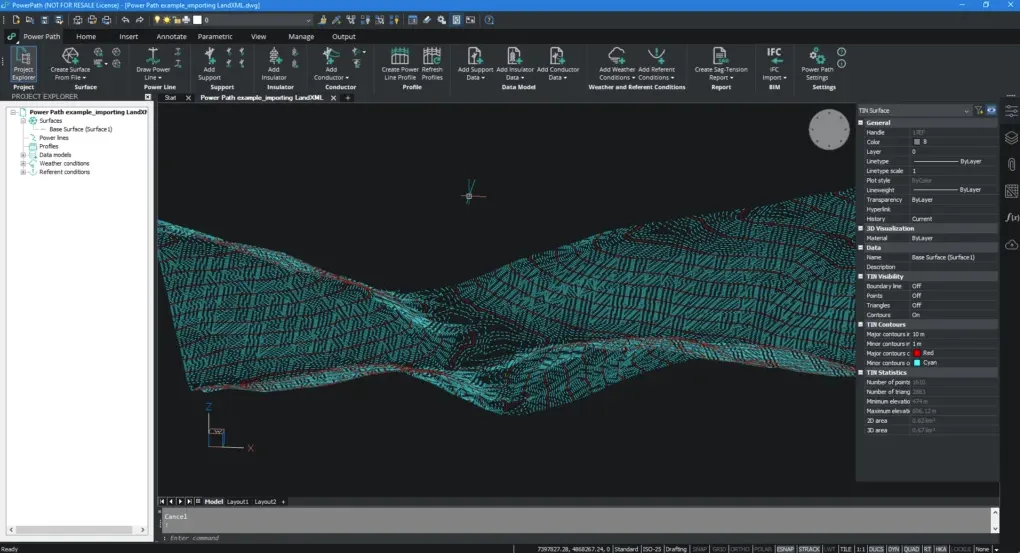

 Service
Service
