Collignon projection
Dec 29,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Collignon projection is a type of equal-area projection (authalic projection) proposed in 1865 by the French mathematician Édouard Collignon. It is designed to represent the entire Earth on a plane, with the key feature of accurately preserving area. It is primarily used for world maps and statistical maps, especially in visualizations that emphasize area comparisons between regions.
Projection Basic
Collignon projection has a relatively simple geometric structure and is composed of the following characteristic elements:
- Projection Surface Shape: A planar projection with a shape close to a square or diamond
- Central Meridian: Typically set at 0° longitude, depicted as a straight line in the north-south direction
- Latitude Lines: The equator is represented as a straight line, while other latitude lines are depicted as curves that bend toward the center
- Longitude Lines: Drawn as straight lines that converge toward the poles, forming an overall radial structure
- Area Preservation Property: Any area on the Earth's surface maintains its original proportional area after projection
Pros
- Accurate Area Representation: As an equal-area projection, it allows for accurate comparisons of the areas of continents or countries.
- Designed for World Maps: Can effectively represent the entire globe on a single map without extreme area distortions.
- Relatively Simple Mathematical Structure: Easy to implement and understand theoretically.
- Suitable for Statistical Maps: Effective for visualizing area-dependent indicators such as population, resource quantities, and land use.
Cons
- Significant Shape Distortion: While area is preserved, shapes are heavily distorted, especially in low-latitude regions.
- Does Not Preserve Angles or Distances: Lacks conformality and equidistance, making it unsuitable for navigation or distance measurement purposes.
- Unsuitable for Local Maps: Not appropriate for high-precision representations of small areas and is primarily limited to global depictions.
- Low General Recognition: Less commonly used as a general map compared to projections like Mercator or Robinson.
Application Scenario
The Collignon projection excels in statistical and comparative maps covering the entire world. It is effective for visually comparing quantitative information based on area, such as population distribution, forest area, agricultural land ratios, and CO₂ emissions by country. It is also used in educational contexts to demonstrate the concept of equal-area projections and serves as a teaching tool to understand the diversity of map projections and the nature of distortions. However, it is rarely adopted in practical maps for navigation or precise surveying purposes.
Example
1. Collignon's world projection.
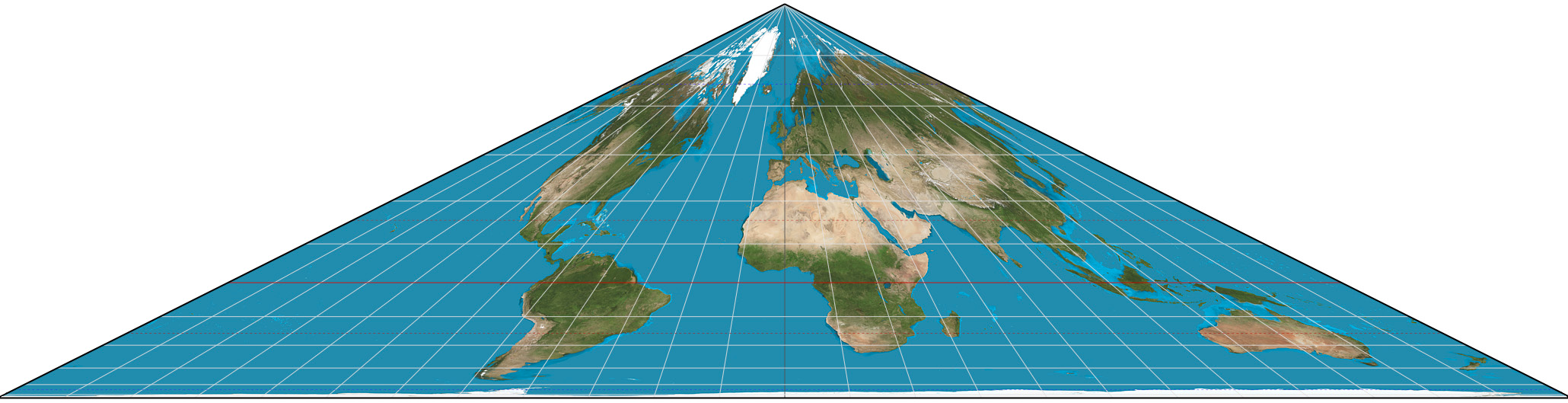
2. Collignon's world projection.
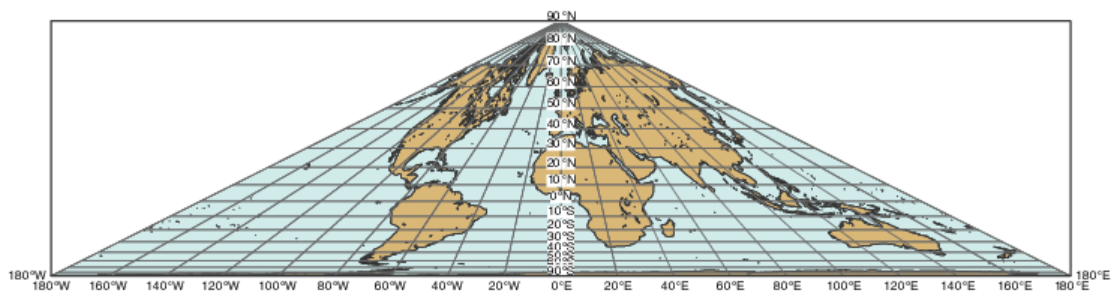
Related GIS Projections
Vertical Near-side Perspective Projection
Two-point Equidistant Projection

 Service
Service
