Equidistant Conic Projection
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Equidistant conic projection is a type of conic projection that projects the Earth onto a conical surface and displays it as a map. It is characterized by keeping the intervals between meridians and parallels constant. In particular, it is designed to minimize distortion of distance along one or two parallels called standard parallels.
In this projection, meridians are drawn as straight lines radiating from the apex of the cone, and parallels are drawn as concentric circular arcs. It is often used for creating maps on a national or continental scale, as it can display large areas on Earth (mainly in the east-west direction) relatively accurately.
Projection Basic
Although the equidistant conic projection cannot perfectly maintain area, shape, and direction, it is suitable for situations where the accuracy of distances in a specific latitude band is important. It is particularly suitable for maps of mid-latitude regions that extend east to west (e.g., North America, Japan, China, etc.), and is often used for educational atlases, geographical materials, administrative planning maps, etc.
Pros
- Distance accuracy: Distances are maintained correctly along standard parallels, and the spacing between meridians and parallels is uniform, making distance measurement easy.
- Ideal for mid-latitude regions: It can display mid-latitude regions extending from east to west in a relatively natural shape.
- Relatively simple projection method: It is mathematically easy to implement, and drawing processing is relatively light.
- Suitable for educational and academic purposes: The structure of latitudes and meridians is visually easy to understand, making it suitable for geography education.
Cons
- Distortion is large in polar regions and low latitude regions: The further the latitude is from the standard parallel, the more pronounced the distortion of shape and area.
- Area is incorrect: Although it is equidistant, it is not equal in area, so it is not suitable for comparing areas.
- Uses are limited: The accuracy is low outside of areas that extend in an east-west direction, so it is not a general-purpose projection method.
- There are issues with maintaining orientation: The direction on the map does not necessarily match the actual orientation.
Application Scenario
The equidistant conic projection is particularly suitable for mapping wide areas located in the mid-latitudes. For example, it is often used for maps that cover a wide area in the east-west direction, such as the entirety of Japan, the United States, and China, and is used in fields where distance is important, such as weather maps, administrative district maps, temperature distribution maps, and road planning maps. It is also suitable for measuring distances on maps and planning routes, and is widely adopted as a projection that combines readability and practicality.
Example
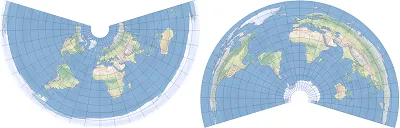
1. Equidistant conic projection.

2. Shows an equidistant or simple conic projection with standard parallels located in the Northern (left) and Southern (right) Hemispheres.
Related GIS Projections
Transverse Mercator Projection
Longitude / Latitude Projection

 Service
Service
