NZMG (New Zealand Map Grid – EPSG:27200)
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
New Zealand Map Grid (NZMG) coordinate system is a projected coordinate system used in New Zealand. Based on the Transverse Mercator projection, it is primarily used for mapping and georeferencing within New Zealand. It projects the Earth's surface onto a flat surface, centered on the South and North Islands of New Zealand. It uses specific central meridians and scale parameters to minimize projection distortion. This coordinate system is widely used in surveying, engineering, and land management in New Zealand. Coordinates are typically expressed in meters, with an origin near the South Island.
Coordinate System Composition
1. Projection Basics: Based on the Transverse Mercator projection, projection distortion is minimized by tangenting a cylindrical surface to the Earth's surface.
2. Parameter Settings: Central meridian is 173°E, scale factor is 0.9996, and false offsets are set to 1,600,000 meters easting and 1,000,000 meters northing.
3. Origin Location: Located near New Zealand's South Island, with specific coordinates of 1,600,000 meters easting and 1,000,000 meters northing.
4. Reference Ellipsoid: The ellipsoid parameters defined by the New Zealand 1949 Geodetic System are used.
Pros
1. Locally Optimized Design: Based on the Transverse Mercator projection, the central meridian (173°E) and scale factor (0.9996) are optimized for the topography of New Zealand's South and North Islands, significantly reducing projection distortion.
2. Engineering Applicability: False offsets (1,600,000 meters easting and 1,000,000 meters northing) ensure positive coordinate values, simplifying calculations and annotations in surveying, mapping, and land management.
3. Uniformity: Utilizing the ellipsoid parameters defined by New Zealand's 1949 Geodetic System, it seamlessly integrates with historical local surveying and mapping data, avoiding errors in multi-coordinate system conversions.
Cons
1. Regional Limitations: Designed specifically for New Zealand, it's not suitable for other regions. International collaboration or global projects require additional conversion to a universal coordinate system like UTM.
2. Lack of Versatility: Compared to the UTM coordinate system, it lacks a zoning mechanism, making it inflexible for expansion outside of New Zealand.
3. Conversion Complexity: Using it across coordinate systems requires specialized tools, which can introduce conversion errors and requires caution, especially in high-precision surveying and mapping.
Application Scenario
The NZMG (New Zealand Map Grid) coordinate system, a New Zealand-specific projection coordinate system, is primarily used in surveying, land management, and engineering projects within New Zealand. This coordinate system utilizes a Transverse Mercator projection (central meridian 173°E) and a false offset design (1,600,000 meters easting and 1,000,000 meters northing) to optimize topographic projection distortion for the South and North Islands, making it a core positioning benchmark for New Zealand's land surveying, cadastral mapping, and infrastructure projects. For example, it is used to accurately delineate plot boundaries in land management and supports construction stakeout for projects such as roads and bridges in engineering surveying. Its metric units simplify local calculation processes. While NZMG lacks global compatibility compared to UTM, its design tailored to New Zealand's geographic characteristics makes it more accurate and practical for local applications.
Example
1. New Zealand map grid (EPSG:27200).
2. New Zealand map grid (EPSG:27200).
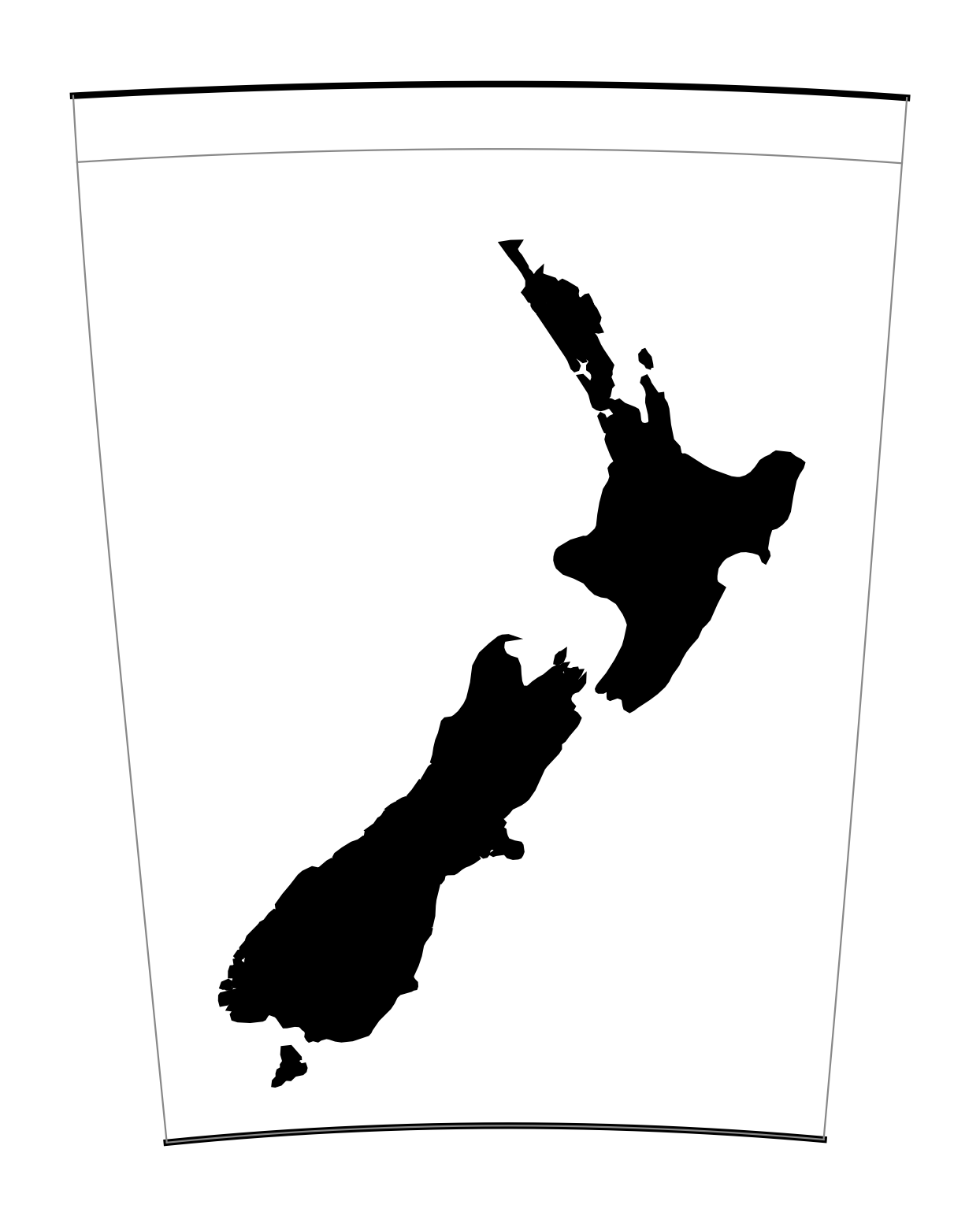
Related GIS Coordinate Systems
References
- https://epsg.io/map#srs=27200-8563&x=6937172704.053008&y=3789748052.964248&z=2&layer=streets
- https://proj.org/en/stable/operations/projections/nzmg.html

 Service
Service
