NTF (Ordnance Survey National Transfer Format)
Nov 24,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Ordnance Survey National Transfer Format (NTF) is a spatial data exchange format developed by the Ordnance Survey (OS) of Great Britain. It is primarily used for the transfer and sharing of cadastral and topographic data. Based on the ISO 8211 standard and employing a binary encoding scheme, it facilitates efficient two-way transfer of national surveying and mapping data between local and central government systems. Its design incorporates three layers—physical file structure, logical model, and application protocol—ensuring the preservation of topological relationships and coordinate system compatibility during data conversion.

File Structure
The file structure of NTF consists of the following components:
- Volume Directory File: This is the first file of the logical volume, used to describe the logical volume and the types of files within it. It also provides information about the arrangement of files in the physical volume where the volume directory file is located.
- Volume Directory Header Record: This is the first record within the volume directory file. It describes the logical volume and provides labeling information for the physical volume. It also includes details such as the number of records, the encoding of the recorded tape, record length, and other relevant information.
- Data Files: These contain the actual topographic data. Each record has a fixed length of 360 bytes, and each data block can contain up to 10 records.
Pros
- Highly standardized: NTF has been selected by the Association for Geographic Information (AGI) in the UK as the preferred format for spatial data exchange, demonstrating strong industry recognition.
- Layered design flexibility: NTF is defined across Levels 1 to 5, supporting the conversion from simple vector data of geological features to complex topological data models, adapting to various application scenarios.
- Topological relationship support: Level 4 is specifically designed for converting fully topological data models, effectively representing dependency relationships between geological and mineral elements.
Cons
- Limited Metadata Support: NTF only transfers the core spatial data and does not include descriptive information such as point symbols, line types, colors, or area fill patterns. These elements must be managed through software controls during input and output processes.
- Restricted Feature Encoding: The format does not fully encompass encoding details for all data models, which may compromise data completeness in certain use cases.
- Narrow Application Scope: Primarily designed for cadastral data exchange within the UK, NTF has limited international adoption and demonstrates low compatibility with mainstream formats like GeoTIFF and DXF.
Application Scenario
NTF is an exchange standard developed by the Ordnance Survey of Great Britain, primarily designed for the bidirectional transfer of national surveying and mapping data between local and central government systems. The format employs a layered structure to organize thematic data such as road networks and water systems, making it suitable for large-scale topographic map conversion. Its core applications include cadastral data exchange and geospatial information sharing, achieving efficient transmission through a binary encoding scheme based on the ISO 8211 standard.
Example
- Mobileye and the UK Topographic Survey have launched a trial of mapping roadside infrastructure in the UK.
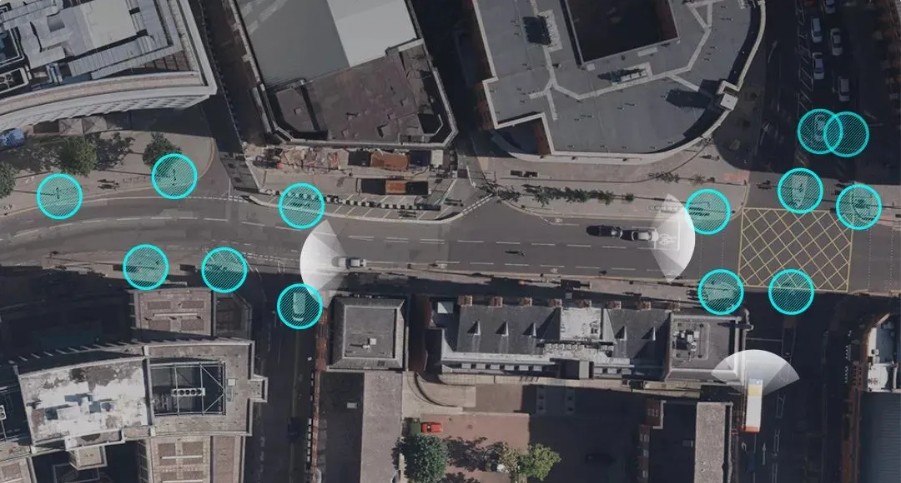

File Opening Mode
- Geographical data for the UK.
Related GIS files
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Transfer_Format
- http://justsolve.archiveteam.org/wiki/National_Transfer_Format
- https://catalyst.earth/catalyst-system-files/enterprise-aerial-help/references/gdb_r/gdb3N292.html

 Service
Service
