Vertical Near-side Perspective Projection
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Vertical Near-Side Perspective Projection is a perspective projection method that observes the Earth from a limited distance (such as a satellite or high altitude) vertically downwards. It simulates the visual effects of the human eye or camera through the center projection method, presenting a sense of depth from near to far. It is commonly used for visualizing satellite images or 3D maps, which can enhance spatial depth perception. However, due to the convergence of projection lines at the viewpoint, it cannot maintain the actual size of objects and is only suitable for intuitive display rather than precise measurement.
Projection Basic
The vertical near side perspective projection adopts the center projection method, which projects the ground point onto the projection plane through the viewpoint (such as satellite position), forming a perspective effect of near large and far small. Its projection lines diverge from the viewpoint, which is different from the parallel projection lines of vertical orthographic projection. It can simulate the stereoscopic effect of real observation, but it will result in a reduction in the proportion of objects farther away from the viewpoint.
Pros
1. Stereoscopic visual effect: Using the center projection method, it simulates the observation perspective of the human eye or satellite, presenting a sense of depth in the near large and far small space, and can intuitively display the three-dimensional form of objects.
2. Strong realism: Suitable for fields such as satellite imagery, 3D maps, architectural design, and advertising art, it can enhance the visual impact and immersion of the scene.
3. Flexibility: In computer graphics, 3D to 2D conversion can be achieved through perspective projection matrices, supporting realistic rendering in fields such as gaming and movies.
Cons
1. Proportional distortion: The projection line diverges from the viewpoint, causing objects farther away from the viewpoint to have a reduced proportion and unable to maintain their actual size, making it unsuitable for precise measurement.
2. The limitations are obvious: it can only display scenes within a 90 ° range from the center of view, and due to the observation distance limitation, distant objects may be severely deformed.
3. High computational complexity: Compared to orthographic projection, its mathematical model and rendering process are more complex, requiring additional processing of vanishing points and perspective deformations.
Application Scenario
Vertical Near side Perspective Projection is widely used in fields that require stereoscopic visual effects and realistic display. In GIS and satellite imagery, it is commonly used to generate stereoscopic effect maps similar to satellite images, simulating the perspective of observing the Earth vertically from a high altitude, enhancing spatial depth perception, but leaning more towards aesthetic display rather than precise measurement. In 3D visualization and computer graphics, this projection achieves the conversion from 3D to 2D through perspective matrices, supporting realistic rendering in fields such as gaming and movies, and is particularly suitable for immersive experiences in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies. In addition, in architectural design, the characteristics of being large in the near and small in the far are utilized to draw renderings, which intuitively display the three-dimensional form and spatial relationships of buildings. In the field of advertising art, the visual impact is used to enhance the expressive power of works.
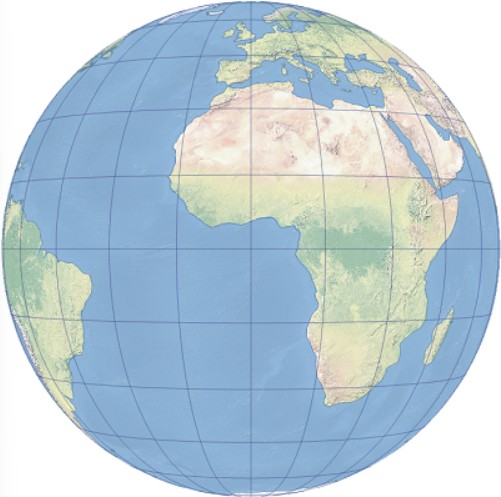
Example
1. Vertical proximal perspective projection centered around Greenwich and the equator.
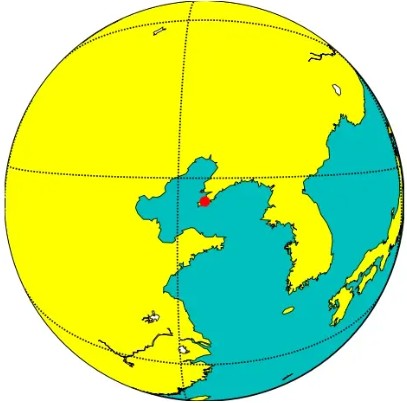
2. Present the Earth's surface centered around a specific central point Dalian.
Related GIS Projections
Transverse Mercator Projection
Longitude / Latitude Projection

 Service
Service
