Eckert Projection
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Eckert projection is a general term for map projections invented by the German geographer Max Eckert in the early 20th century. He developed six projections (Eckert I to Eckert VI) with different characteristics, each of which represents the Earth's surface from a different perspective. These projections are mainly classified as pseudocylindrical projections, and Eckert IV and VI in particular are widely used in education and geographical materials due to their area accuracy (equal area) and good visual balance.
Projection Basic
The Eckert projection aims to visualize the entire Earth in a relatively uniform shape by representing parallels as horizontal straight lines and meridians as curved or straight lines.
The following two types are particularly representative:
- Eckert IV: An equal-area projection that is designed to minimize distortion of the shape while accurately maintaining the area ratio of the Earth. The meridians are slightly curved, giving it a natural and soft appearance.
- Eckert VI: Also an equal-area projection, the parallels are equally spaced straight lines and the meridians are curved, reducing distortion in the polar regions. Overall, it has a very smooth elliptical appearance and is well-known for its visual beauty.
Pros
- Equal-area: Eckert IV and VI maintain area accurately, making them suitable for comparing land areas.
- Good visual balance: Extreme shape distortion is suppressed, and the entire Earth is depicted in a natural, smooth shape.
- Suitable for educational purposes: They are often used in schools and teaching materials because they can clearly show the extent of the entire world.
- Less exaggeration of polar regions: Eckert VI improves visual balance by compressing the polar regions.
Cons
- Distortion of angles and distances: The cost of maintaining accurate area is that directions and distances are not accurately represented.
- Not suitable for navigational purposes: Distortion of direction makes it unsuitable for precise route planning.
- Not suitable for precise analysis of topography: It is not suitable for analyses that emphasize fine shapes and distances, so there are limitations to precise GIS analysis.
Application Scenario
The Eckert projection is ideal for representing macroscopic data overlooking the world, such as in geography education, statistical maps, population distribution maps, and visualization of climate zones. Eckert IV and VI are particularly popular for themes that require accurate area (such as deforestation, land use, and energy consumption by country). In addition, its visually neat shape makes it suitable for reports and exhibition materials, and it is highly valued as a map that combines good appearance with information.
Example
1. Eckert I projection.
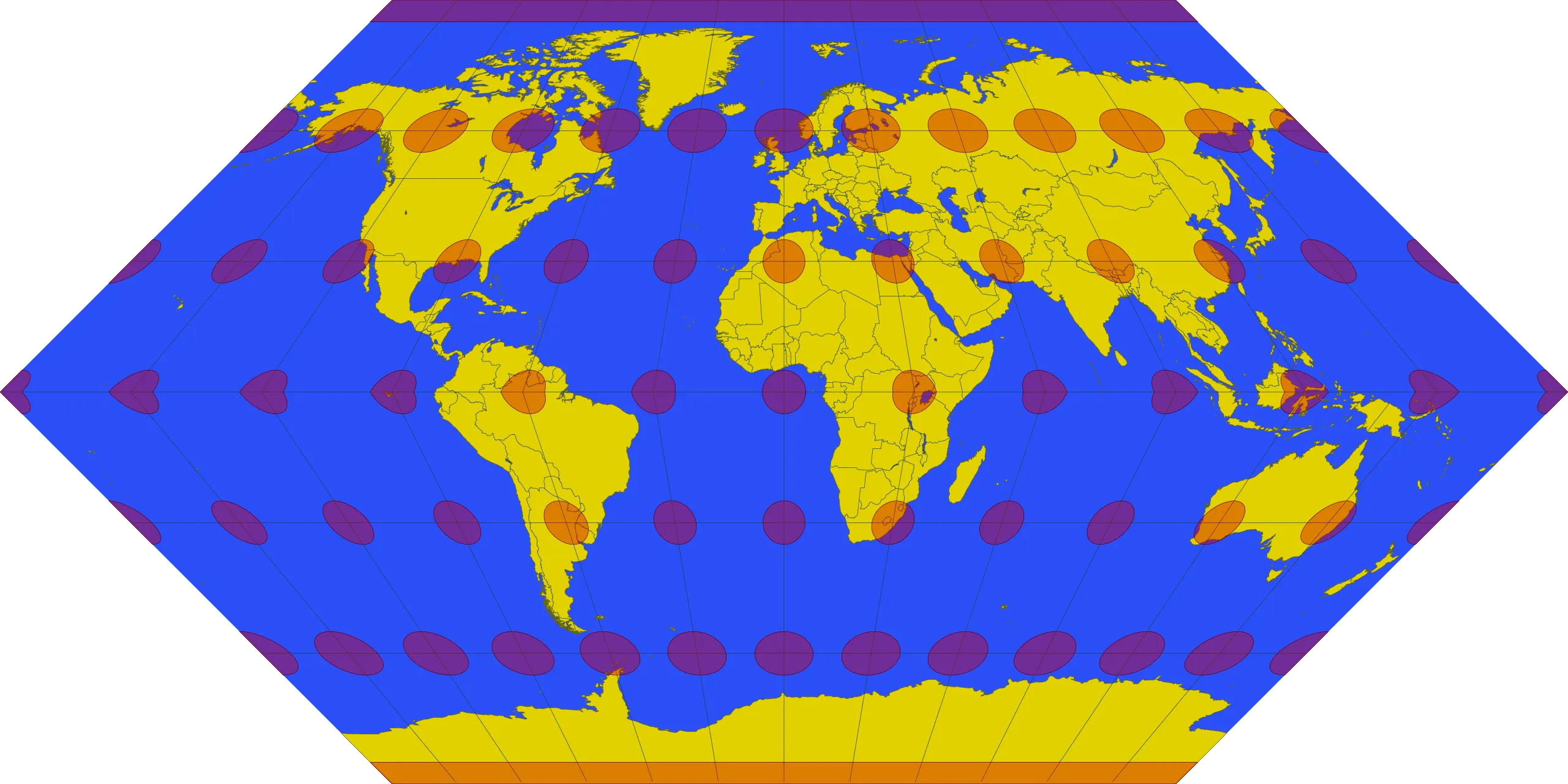
2. Eckert IV projection.
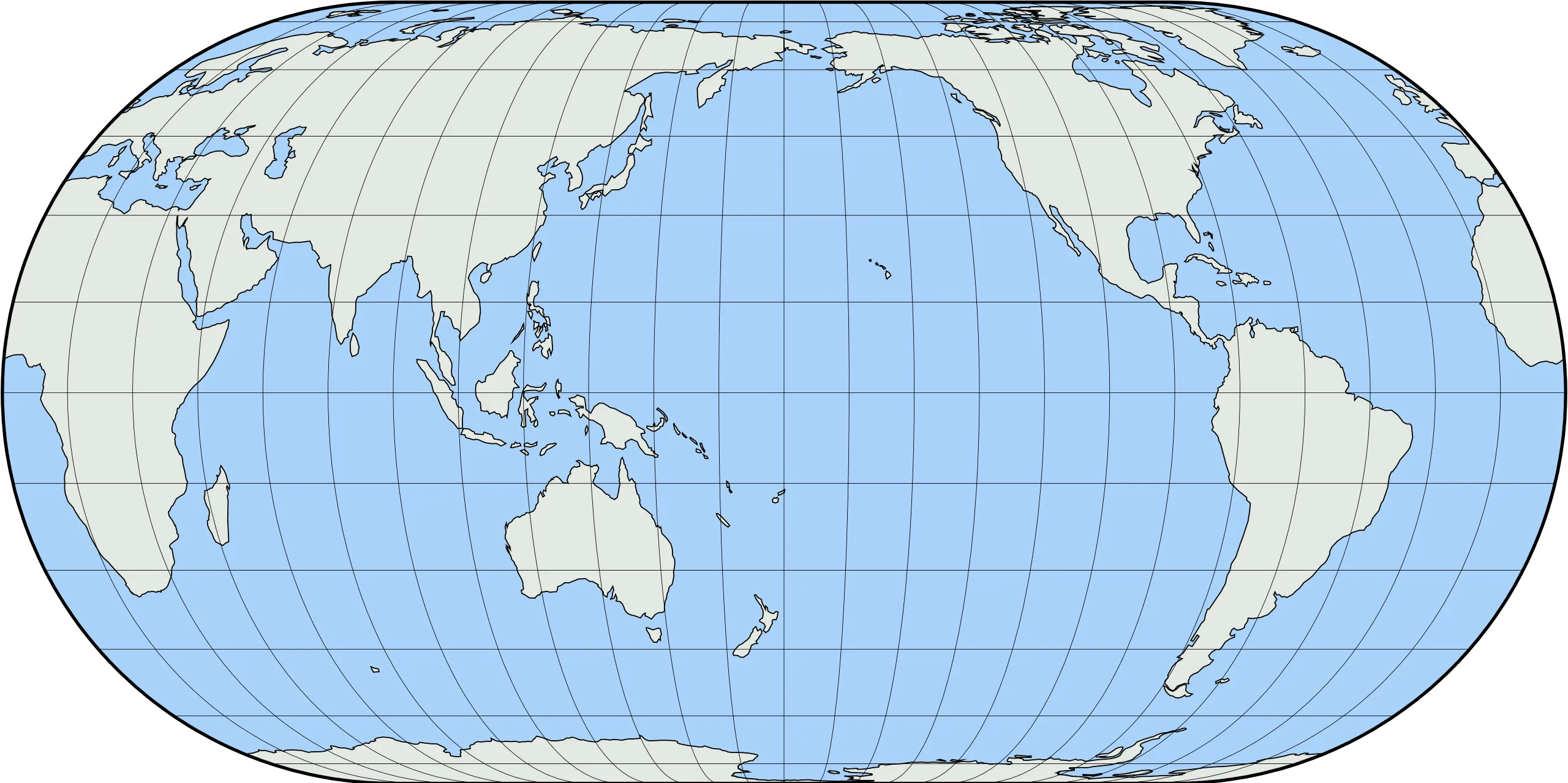
Related GIS Projections
Transverse Mercator Projection
Longitude / Latitude Projection

 Service
Service
