Craster Parabolic Projection
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Craster parabolic projection is a type of map projection classified as a pseudo-cylindrical projection that projects the Earth's surface onto a flat surface in a manner that approximates the shape of a parabola. This method was invented by John Craster in 1910 and is primarily used to create world maps. The map's parallels are straight and evenly spaced, while the meridians, except for the central meridian, are parabolic. It achieves a relatively smooth visual balance while minimizing area distortion, making it suitable for educational materials and visually easy-to-understand globe displays.
Projection Basic
The Craster Parabolic Projection divides the Earth into three zones in the east-west direction and arranges the meridians as smooth parabolas within each zone. As a result, the overall map takes on a gently curved shape, avoiding extreme distortions. The central meridian is depicted as a straight line, with each meridian spreading out parabolically from this reference. It has the following characteristics:
- Area is maintained relatively accurately (pseudo-equal-area property).
- Since parallels of latitude are parallel and evenly spaced, it is easy to compare latitudes.
- The entire map features smooth, natural curves, offering aesthetic appeal.
- While distortion in polar regions is minimized, it does not preserve shapes with perfect accuracy.
Pros
- Excellent visual balance: With no extreme stretching, it features a smooth overall appearance, making it suitable for educational and display purposes.
- Minimal area distortion: As a pseudo-equal-area projection, it is well-suited for comparing areas across different regions.
- High visibility of the central meridian: The straight depiction of the central meridian makes it easy to understand the map's structure using this reference line.
- Relatively simple mathematical formulas: Compared to other complex projections, its equations are straightforward, facilitating easier implementation.
Cons
- Lacks accuracy in shape representation: Shape distortion tends to occur easily, particularly in high-latitude regions.
- Reduced visibility due to parabolic meridian shapes: Since meridians are not straight lines, it can sometimes be difficult to grasp distances in the east-west direction.
- Unsuitable for navigation purposes: It is not well-suited for applications that require precise angle or distance measurements.
Application Scenario
Due to its balanced visual representation, the cluster parabolic projection is primarily used for world map educational posters, illustrated books, and visualization of international statistical data. In geography education, it is a popular teaching material for understanding the overall world picture without extreme distortion, and is suitable for roughly showing the Earth's area distribution and continental layout. In GIS software, it is also sometimes applied to visual materials such as the visualization of global environmental data and global warming maps, taking advantage of its lightweight processing and area-preserving characteristics.
Example
1. Craster parabolic projection example.
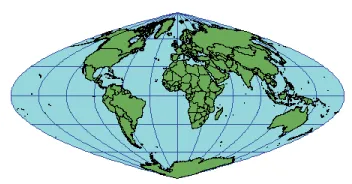
2. Craster parabolic projection example.
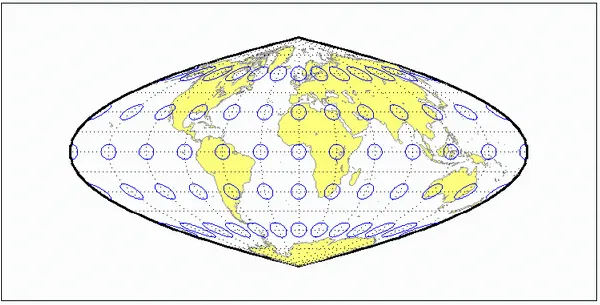
Related GIS Projections
Transverse Mercator Projection
Longitude / Latitude Projection

 Service
Service
