POSGAR 2007 (Argentine National Geodetic Datum - EPSG:5342)
Nov 5,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
POSGAR 2007 is the geodetic reference system used by Argentina. It is an ellipsoid-based geographic coordinate system used to accurately describe spatial locations within the country. Based on the GRS80 ellipsoid, this coordinate system uses specific projection parameters (such as UTM Zone 19S) to achieve regional positioning. It primarily serves the fields of land surveying and mapping, engineering construction, and natural resource management. Its core feature is that it is optimized for Argentina's geographical characteristics. Minor differences exist with the WGS84 coordinate system, requiring parameter conversion for data interoperability.
Coordinate System Composition
- Datum and Ellipsoid: The GRS80 ellipsoid is used as the datum, with a semi-major axis of 6,378,137 meters and an oblateness of 1/298.257222101. It is centered at the Earth's center of mass and is suitable for high-precision global measurements.
- Projection: The UTM Zone 19S Transverse Mercator projection is used, with the central meridian at 75° West, covering central and eastern Argentina. Projected coordinates are in meters to minimize local distortion.
- Coordinate Units and Elevation Datum: Plane rectangular coordinates (easting and northing) are in meters. Elevation datums may use the EGM96 Earth Gravity Model or an ellipsoidal reference.
- Conversions to Other Coordinate Systems: Conversions to WGS84 are done using the seven-parameter or three-parameter models. Conversions to other South American coordinate systems (such as SIRGAS 2000) rely on public parameters published by the Argentinian Surveying and Cartography Agency.
Pros
- Optimized Regional Applicability: POSGAR 2007 is based on the GRS80 ellipsoid and uses the UTM Zone 19S projection (central meridian 75° West) to adjust parameters for the geographical features of central and eastern Argentina. This significantly reduces localized distortion, making it particularly suitable for the country's land surveying and engineering surveying needs.
- High-Precision Surveying Capabilities: Utilizing a geocentric datum (GRS80 ellipsoid) and modern projection technology, it achieves millimeter-level surveying accuracy, meeting the high-precision spatial data requirements of natural resource management, infrastructure development, and other applications.
- Standardization and Compatibility: As Argentina's official national coordinate system, POSGAR 2007 utilizes a seven-parameter model to achieve interoperability with global coordinate systems such as WGS84, facilitating international project collaboration and the local application of data from satellite navigation systems (such as GPS).
Cons
- Complexity of International Data Conversion: Conversion to other regional coordinate systems in South America (such as SIRGAS 2000) relies on officially released conversion parameters from Argentina, increasing the difficulty and cost of cross-border data integration. Non-expert users may face difficulties in obtaining these parameters and technical barriers to entry.
- Global Coverage Limitations: As a regional coordinate system, its UTM projection only covers central and eastern Argentina (Zone 19S) and is not applicable to western Argentina or other regions globally.
- Risk of Lagging Technology Updates: Compared to dynamically updated global geocentric coordinate systems (such as ITRF), the datum parameters of POSGAR 2007 are fixed. Long-term use may lead to accumulated errors due to geophysical changes (such as plate tectonics), necessitating regular parameter revisions.
Application Scenario
The POSGAR 2007 coordinate system is primarily used in land surveying, engineering construction, and natural resource management in Argentina. Based on the GRS80 ellipsoid and the UTM Zone 19S projection, it is particularly well-suited for the high-precision surveying needs of central and eastern Argentina. This coordinate system plays a vital role in infrastructure construction (such as road and bridge planning), land resource surveys, geological exploration, and environmental monitoring. Furthermore, its compatibility with global coordinate systems (such as WGS84) through parameter conversion facilitates international project collaboration.
Example
1. Argentine quasi-coordinate system.
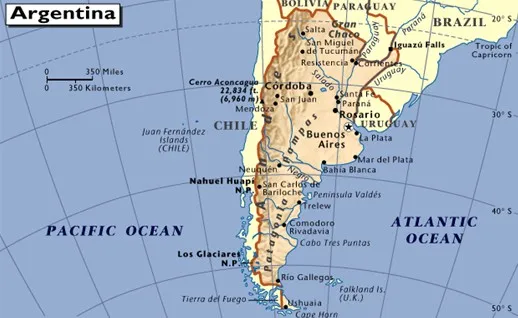
2. Coverage Area - Provided by MapTiler.
_1763977472166.png)

 Service
Service
