Gnomonic Projection
Nov 24,2025
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Gnomonic Projection is a perspective azimuthal projection that uses the center of the sphere as the light source. It projects great circles on the spherical surface (such as meridians and the equator) as straight lines, making it commonly used in navigation, astronomy, and seismic analysis. Its key characteristic is the absence of distortion at the projection center, but extreme distortion occurs at the edges. While suitable for mapping great-circle routes or analyzing linear paths, it does not preserve area or angular relationships.
Projection Basic
The Gnomonic Projection is a perspective azimuthal projection that projects great circles (e.g., meridians and the equator) as straight lines by geometrically mapping spherical points onto a tangent plane with the light source at the sphere's center. Distortion is minimal at the projection center but increases drastically toward the edges. This projection is ideal for plotting great-circle routes or analyzing straight-line paths but cannot maintain accurate area or angle representations.
Pros
- Intuitive Visualization: Based on geometric perspective principles, it aligns with human visual intuition when transforming spherical surfaces to a plane.
- Great-Circle Linearity: Projects great circles (e.g., the shortest navigation routes) as straight lines, facilitating maritime and aerial navigation.
- Zero Distortion at Center: The central region (near the tangent point) exhibits no length or angular distortion, making it suitable for localized precision analysis.
Cons
- Extreme Edge Distortion: Length and area distortions increase dramatically away from the projection center, approaching infinity at the edges.
- Non-Equal-Area and Non-Conformal: Fails to preserve area or angular relationships, rendering it unsuitable for maps requiring precise measurements of size or shape.
- Limited Applicability: Only practical for small areas or specific purposes (e.g., route planning) and inappropriate for world maps or large-scale cartography.
Application Scenario
The Gnomonic Projection is widely used in maritime and aerial navigation for planning the shortest great-circle routes due to its ability to represent spherical great circles as straight lines. It is also employed in seismic wave path analysis, helping scientists study the propagation patterns of seismic waves along Earth's great circles. In astronomy, this projection aids in analyzing celestial motion trajectories, such as the great-circle paths of the ecliptic or planetary orbits.
Example
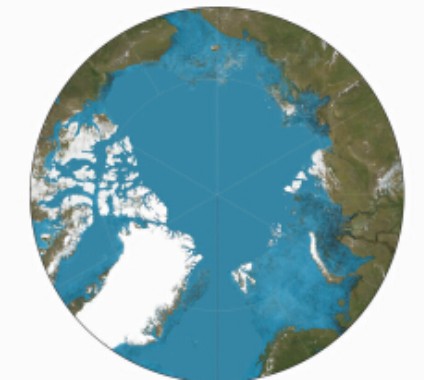
1. A schematic diagram of a sundial projection within the Arctic Circle.
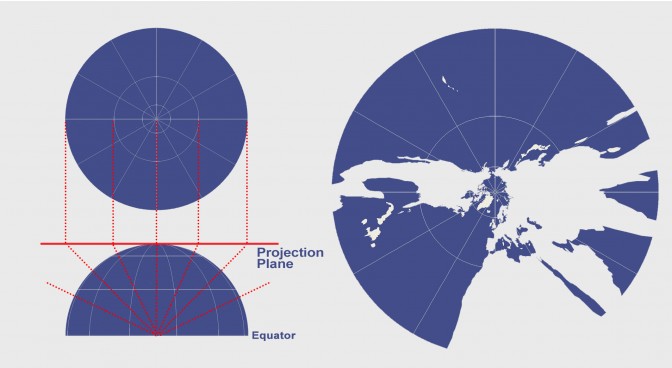
2. Geocentric projection (Gnomonic projection).
Related GIS Projections
Transverse Mercator Projection
Longitude / Latitude Projection

 Service
Service
