Greek Grid (Greek National Coordinate System – EPSG:2100)
Greek Grid is a plane rectangular coordinate system based on a projection specific to Greece, a type of geographic grid coordinate system (GRID). It divides the Earth's surface into virtual grid lines, projecting spatial coordinates onto a plane to form a locally applicable coordinate system. It is commonly used in mapping and engineering surveying in Greece. Unlike universal geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude), this coordinate system directly represents plane positions using x and y values, making it suitable for precise positioning in small areas.
2025-11-05 15:05:37Lambert-93 (French Lambert 93 coordinate system - EPSG:2154)
Lambert-93 is the projection coordinate system used by the French National Geographic Information System (IGN). A variant of the Lambert Conformal Conic projection, it is based on the WGS 84 ellipsoid and is suitable for planimetric mapping of metropolitan France and surrounding areas. It features dual standard parallels (44° and 49° North) to reduce distortion. Coordinates are expressed in meters and are commonly used in topographic mapping, land management, and GIS data integration. Compared to the UTM or Gauss-Krüger projections, this coordinate system is more suitable for conformal mapping requirements in mid-latitudes.
2025-11-05 15:04:45POSGAR 2007 (Argentine National Geodetic Datum - EPSG:5342)
POSGAR 2007 is the geodetic reference system used by Argentina. It is an ellipsoid-based geographic coordinate system used to accurately describe spatial locations within the country. Based on the GRS80 ellipsoid, this coordinate system uses specific projection parameters (such as UTM Zone 19S) to achieve regional positioning. It primarily serves the fields of land surveying and mapping, engineering construction, and natural resource management. Its core feature is that it is optimized for Argentina's geographical characteristics. Minor differences exist with the WGS84 coordinate system, requiring parameter conversion for data interoperability.
2025-11-05 15:03:01RSO91 (Revised Saberang Ordnance Survey 1991, EPSG:29873)
RSO91 (Revised Saberang Ordnance Survey 1991, EPSG:29873) is the geodetic datum and projected coordinate system for the Malaysian state of Sabah (northern Borneo). This coordinate system has been adapted to suit the local topography and geodetic environment, and is widely used for infrastructure development, land management, cadastral surveys, and environmental monitoring, particularly in Sabah. RSO91 is a revised and updated version of the previously used RSO (Revised Saberang Ordnance Survey) coordinate system, and is intended to provide a more accurate location reference.
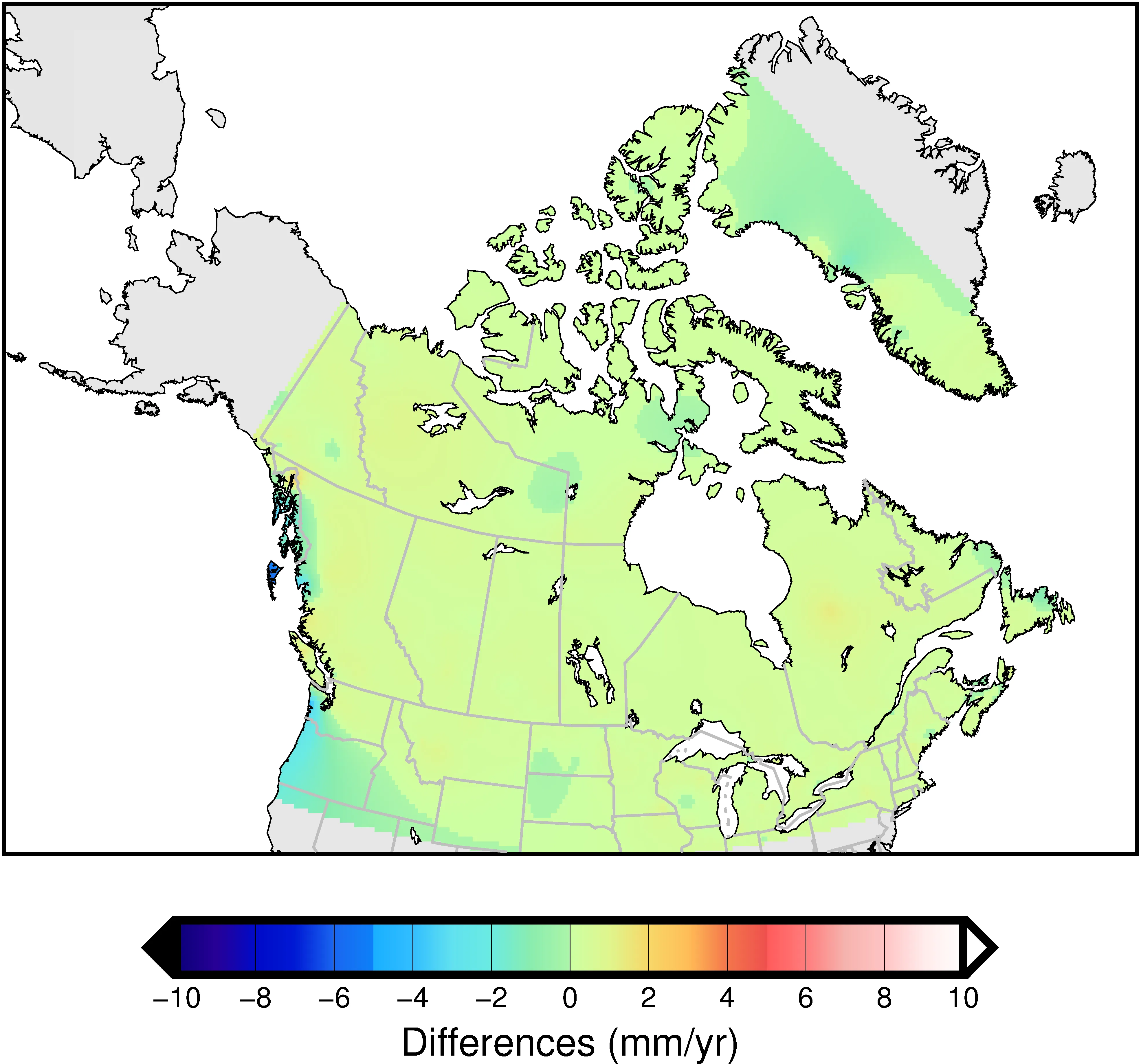
2025-11-05 15:02:13NAD83 (CSRS) (North American Datum 1983 – Canadian Spatial Reference System)
NAD83 (CSRS) (North American Datum 1983 – Canadian Spatial Reference System) is a geographic coordinate reference system for all of Canada, with EPSG code 4617. Managed and maintained by Natural Resources Canada (NRCan), it is based on the North American Datum (NAD83) and has been improved to improve the accuracy of Canada's geodetic network. The CSRS version reflects crustal movements and resurvey results of geodetic control points, improving positioning accuracy and consistency. It is widely used in surveying, geographic information systems (GIS), and global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) in Canada.
2025-11-05 15:01:08GGRS87 (Greek Geodetic Reference System 1987)
GGRS87 (Greek Geodetic Reference System 1987) is a geodetic reference system for geographic information processing covering the whole of Greece. Its EPSG code is 4120 and is widely used for domestic spatial information management, primarily for topographic mapping, surveying, cadastral management, and infrastructure development. This coordinate system is designed to optimize positional accuracy within the Greek territory while maintaining high compatibility with the European Geodetic System (ETRS89) and the World Geodetic System (WGS84).
2025-11-05 15:00:18Hartebeesthoek94 (EPSG:4148)
Hartebeesthoek94 (EPSG:4148) is a geographic coordinate system covering all of South Africa and has been adopted as the country's national geodetic standard. This coordinate system is based on the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF), which uses the Earth's center of gravity, and was introduced in 1994. Its primary purpose is to obtain and use accurate location information within South Africa for purposes such as mapping, surveying, infrastructure management, and disaster prevention. It is highly compatible with GNSS (particularly GPS) and provides positional accuracy that takes into account the effects of long-term crustal movement, making it also useful for geological surveys and wide-area surveys.
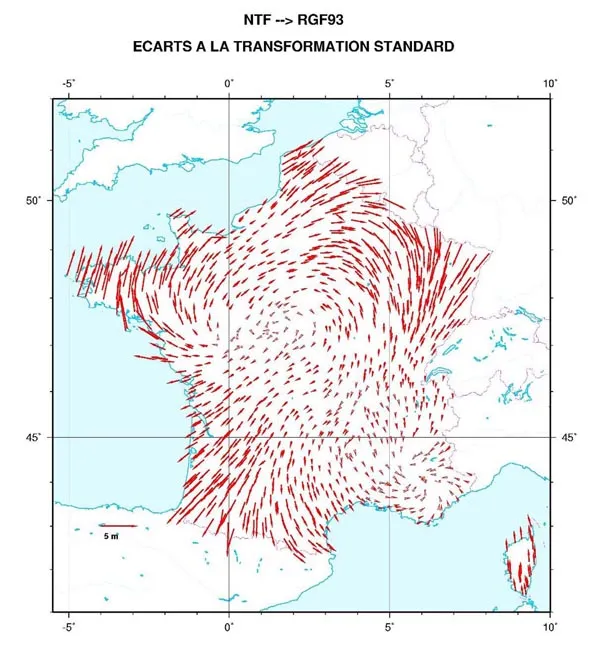
2025-11-05 14:59:23GF93 (Référentiel Géodésique Français 1993 | EPSG:4171)
RGF93 (Référentiel Géodésique Français 1993 | EPSG:4171) is the geodetic reference system adopted as the location standard for geospatial data throughout France. It is based on the international geodetic standard ITRF (International Terrestrial Reference Frame) and aims to unify geographic information and provide high-precision positioning throughout France and its overseas territories. RGF93 is widely used as a standard foundation to ensure positional accuracy and consistency in GPS observations and spatial analysis in geographic information systems (GIS).
2025-11-05 14:58:30ETRS89-LAEA (EPSG:3035)
ETRS89-LAEA is a geographic coordinate system formed by combining the European Terrestrial Reference System (ETRS89) with the Lambert Azimuthal Equal Area Projection (LAEA), which is mainly used for spatial data unification within the European Union. It takes the center of the earth as the origin and uses an equal area projection to keep the area unchanged, making it suitable for large-scale statistical analysis and environmental monitoring. This coordinate system is promoted by the European Organization for Surveying and Mapping (EUROSTAT) and is one of the standardized projections recommended by the INSPIRE directive.
2025-11-05 14:57:26Lambert Conformal Conic (EPSG:Multi-region code)
Lambert Conformal Conic is a conformal conic projection coordinate system proposed by German mathematician Lambert. It projects the earth's surface onto a cone surface, keeping the angle unchanged but with length deformation. It is often used for mapping in mid-latitude areas. The coordinate system is divided into two forms: the positive axis (symmetric along the standard parallel) and the oblique axis, which is suitable for map applications with moderate regional scope.
2025-11-05 14:50:01
 Service
Service



_1762326164221.png)
_1762326047605.png)
_1762326009261.png)
_1762325889900.png)
_1762325433379.png)