Jordan TM (Jordan Transverse Mercator | EPSG:3144)
Jordan TM (Jordan Transverse Mercator | EPSG:3144) is a projected coordinate system officially adopted by the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan for national mapping and surveying purposes. Developed under British technical influence during the mid-20th century, this system serves as Jordan's primary framework for topographic mapping, land administration, and infrastructure development. While modern GNSS-compatible systems are increasingly utilized, Jordan TM remains essential for interpreting historical geographic data and maintaining continuity in the country's geospatial records.
2026-01-23 15:03:48Israel TM Grid (Israeli National Grid | EPSG:2039)
Israel TM Grid (Israeli National Grid | EPSG:2039) is the official national projected coordinate system adopted by Israel, primarily used for surveying, mapping, and engineering construction within the country. This coordinate system is based on the Israeli national surveying system and employs a Transverse Mercator projection to facilitate precise measurements and map compilation in Israel and its surrounding regions. Although global positioning systems (such as WGS84) have gained widespread use, the Israel TM Grid remains highly valuable for local engineering, land management, and historical geospatial data applications.
2026-01-23 14:56:26Hong Kong 1980 Grid (Hong Kong 1980 Coordinate System | EPSG:2326)
Hong Kong 1980 Grid (Hong Kong 1980 Coordinate System | EPSG:2326) is a regional projected coordinate system specially designed for Hong Kong's urban surveying and mapping needs during the late 20th century. Developed as part of Hong Kong's territorial surveying framework, this system employs a transverse Mercator projection centered on the region's specific geographical characteristics. Although now supplemented and partially superseded by modern geocentric systems, it remains crucial for processing legacy engineering plans, cadastral records, and historical urban data from Hong Kong's development boom period.
2026-01-23 14:41:38Xian 1980 (Xi'an 1980 Coordinate System | EPSG:4610)
Xian 1980 (Xi'an 1980 Coordinate System | EPSG:4610) is a Chinese national geodetic datum established in the 1980s as an improved successor to the Beijing 1954 system. It was developed to address the limitations of the earlier non-geocentric datum and to better support China's growing surveying, mapping, and infrastructure needs. Based on the IAG 1975 ellipsoid with a geocentric origin, Xian 1980 represented a significant step toward modern geodetic standards in China. Although now superseded by the fully geocentric CGCS2000, it remains important for processing data from the late 20th century and serves as a transitional benchmark in China's geodetic evolution.
2026-01-23 14:34:34Beijing 1954 (Beijing 1954 Coordinate System, EPSG:4214)
Beijing 1954 (Beijing 1954 Coordinate System, EPSG:4214) is a national geodetic datum established in China during the 1950s. As the first nationwide unified coordinate system introduced after the founding of the People’s Republic of China, it is a non-geocentric (local) datum designed for nationwide surveying and mapping. It was developed with reference to the Soviet geodetic framework and is based on the Krasovsky 1940 ellipsoid. This coordinate system was used extensively across China for foundational surveying, topographic mapping, infrastructure construction, and land administration over a long period, forming the basis of China's surveying and mapping system in the latter half of the 20th century. Although it has now been officially replaced by the more precise and geocentric CGCS2000, it still plays a significant role in processing historical and legacy data.
2026-01-23 14:25:04Batavia (Batavia Datum | EPSG:4211)
Batavia (Batavia Datum | EPSG:4211) is a region-specific, non-geocentric datum used primarily in the former Dutch East Indies (present-day Indonesia) during the early 20th century. Established to support colonial administration, topographic surveying, cadastral mapping, and infrastructure development, it served as a unified reference for surveying and mapping centered around Java. Today, it has been entirely replaced by modern geocentric coordinate systems such as ITRF and WGS84. Its practical relevance is now largely confined to the conversion and analysis of historical maps and legacy survey data.
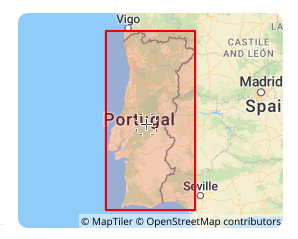
2026-01-23 14:17:47Lisbon 1890 (EPSG:4803)
Lisbon 1890 (EPSG:4803) is a regional non-geocentric datum established by Portugal at the end of the 19th century. It primarily provided a unified coordinate framework for the country's early terrestrial surveying and topographic mapping (for example, when combined with the Bonne projection to form EPSG:2963). As a national standard from a specific historical period, it has been completely superseded by modern geocentric datums (e.g., ETRS89). Its current value is limited solely to processing and converting legacy Portuguese data such as historical maps and cadastral archives from the late 19th to mid-20th century, which, after professional conversion, can be used for digital archiving and historical geographic analysis.
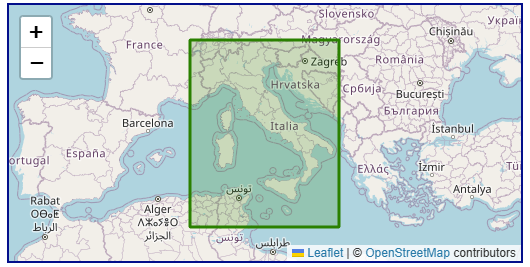
2025-12-29 16:45:37Roma40 (Rome 1940, EPSG:4806)
Roma40 (Rome 1940, EPSG:4806) is a regional, historical geodetic datum designed specifically for Italy and its surrounding regions (such as Sicily and Sardinia), and belongs to the geocentric coordinate system. Its core purpose was to provide a benchmark for official Italian surveying from the 1940s to the 1990s.
2025-12-29 16:38:56ED87 (European Datum 1987, EPSG:4231)
ED87 (European Datum 1987, EPSG:4231) is a regional geodetic datum established in 1987 specifically for Europe, primarily Western Europe. It is a traditional geodetic datum designed to align the coordinate framework as closely as possible with the European geoid at the time and served as a key intermediate achievement in the modernization of European geodesy. Its primary application is in processing historical surveying data, topographic maps, and engineering drawings from Western Europe predating the 1990s. However, as a transitional datum based on terrestrial triangulation, its accuracy and global compatibility are now insufficient. Today, it is mainly used for scenarios such as historical data integration, digital archiving, and specialized research after being transformed into modern geocentric coordinate systems like WGS84 or ETRS89.
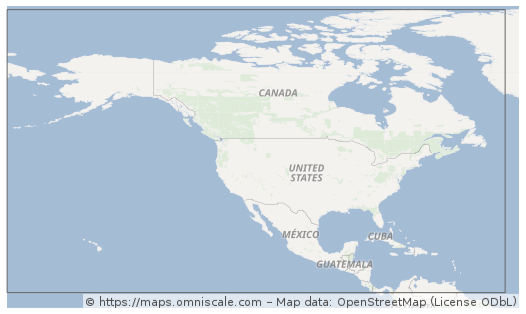
2025-12-29 16:30:44NAD27 (North American Datum 1927)
NAD27 (North American Datum 1927) is a geodetic datum established in 1927 for North America, defined based on the Clarke 1866 ellipsoid with its origin at Meades Ranch in Kansas, USA. This datum served as the official mapping and surveying standard for the United States, Canada, and Mexico for decades, widely used in historical topographic maps, land ownership records, and traditional geographic data. Although its accuracy is limited by early surveying technology and it has been superseded by more modern datums (e.g., NAD83), a significant number of historical archives and legacy systems still rely on NAD27. Therefore, special attention must be paid to datum transformations when dealing with older geographic data in North America.
2025-12-29 16:04:49
 Service
Service