SIRGAS 2000 (South American Datum | EPSG:4674)
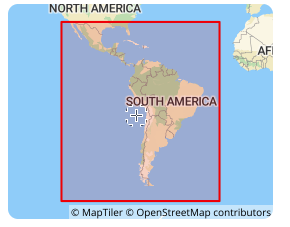
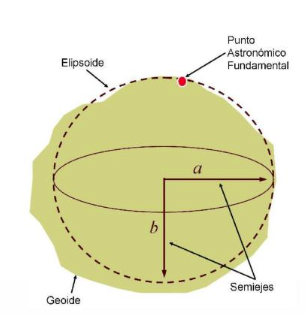
**SIRGAS 2000 **is a geocentric reference frame for Central and South America, which aims to define and implement a unified reference frame for Central and South America that is consistent with ITRF. Its ellipsoid adopts GRS 1980, with a major semi-axis of 6378137 meters, an oblateness of 298.257222101, the Greenwich meridian as the prime meridian, and the angle unit is degree. SIRGAS 2000 was established in 2000, consistent with the ITRF2000 framework, with a reference epoch of 2000.0. It is a regional encryption of ITRS in South America, achieved through a network of about 200 continuously operating stations (SIRGAS-CON) throughout Latin America and the Caribbean.
2025-09-16 14:47:10European Datum 1950 | EPSG:4230 (ED50)
ED50 is a European geodetic datum established in 1950. It is based on the overall adjustment of the European triangulated network and adopts Clarke ellipsoid parameters. It is mainly used for topographic surveying, mapping and early geographic information system (GIS) applications in Europe.
2025-09-16 14:47:07JGD2011 (Japanese Geodetic Datum 2011 | EPSG:6668)
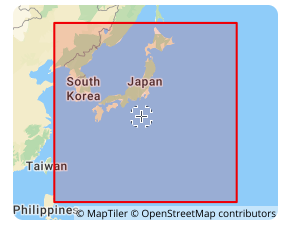
JGD2011 is a modern geocentric coordinate reference frame established by Japan in the early 21st century to replace the old Tokyo Datum (such as Tokyo 1918). Its core is based on the GRS80 ellipsoid, with the origin aligned with the center of mass of the earth, and the coordinate axis pointing in accordance with international standards (such as the prime meridian passing through Greenwich). This framework is implemented through space geodetic technologies such as GNSS and VLBI, with an accuracy of centimeters. It can dynamically reflect plate movement and earth deformation, and is suitable for high-precision geographic positioning needs in Japan and surrounding waters, and is gradually connected with international coordinate systems (such as ITRF).
2025-09-16 14:47:08MGI (Militar-Geographische Institut | EPSG:4312)
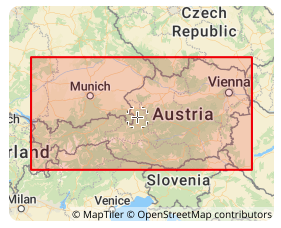
MGI coordinate system was established by the Austrian Military Geographical Institute. It is a local coordinate system based on the Bessel ellipsoid and is mainly used for geographic information representation and spatial positioning in Austria. It uses the Transverse Mercator projection, with the central meridian at 13°20′ east longitude, the latitude of the projection origin at 0°, the easting offset of 1,500,000 meters, and the northing offset of 0 meters. It is a variant of the Gauss-Krüger projection and is widely used in Austria in many fields such as topographic mapping, land management, urban planning, and transportation planning, providing an accurate spatial reference frame for these fields.
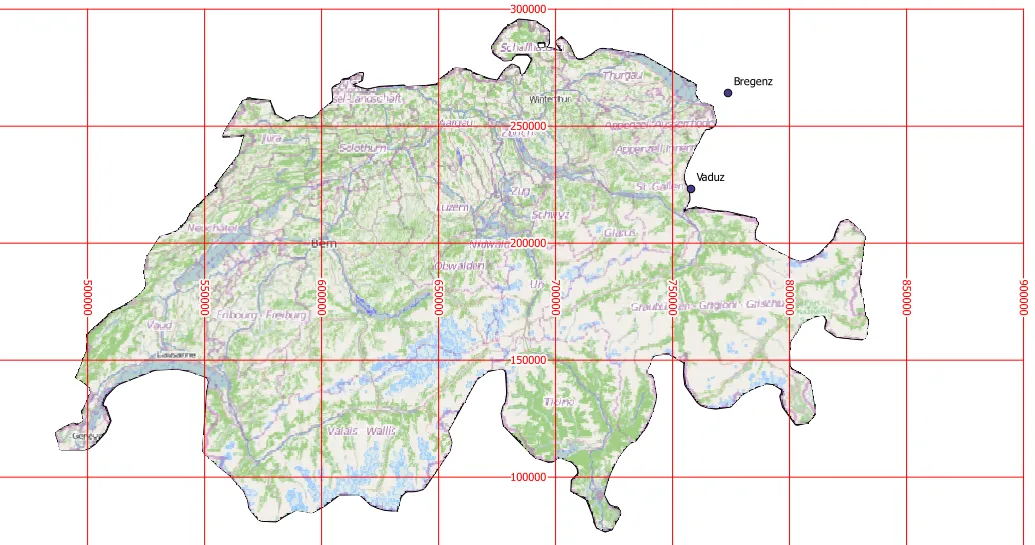
2025-09-16 14:47:10CH1903 (Swiss Coordinate System 1903 | EPSG:4149)
CH1903 is the widely used national coordinate system of Switzerland, based on the geodetic datum established in 1903. It is a projection coordinate system covering the whole of Switzerland, developed to enable precise geospatial information management and mapping of a country with mountainous terrain. The reference ellipsoid used is Bessel 1841, and the projection method is the Oblique Mercator Projection. This coordinate system has long been used by the Swiss National Cartographic Office (Swisstopo) and has become a standard in many fields such as topographic mapping, surveying, civil engineering and infrastructure planning. In recent years, Switzerland has gradually transitioned to the higher-precision CH1903+ (EPSG:2056) coordinate system, but a large amount of historical data is still stored based on CH1903.
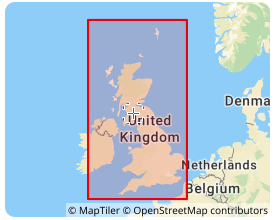
2025-09-16 14:47:11OSGB36 (Ordnance Survey Great Britain 1936 | EPSG:4277)
OSGB36 is the UK national coordinate system, the full name is Ordnance Survey Great Britain 1936, and its EPSG code is 4277. This coordinate system is based on the Airy 1830 ellipsoid and was developed by the Ordnance Survey of the United Kingdom. It is the national datum for topographic surveying in the United Kingdom. In the fields of geographic information systems (GIS), cartography, and engineering surveying in the United Kingdom, OSGB36 has been widely used, providing a unified reference framework for geospatial data in the United Kingdom, allowing geographic data from different sources to be integrated and analyzed in the same coordinate system.
2025-09-16 14:47:10China Geodetic Coordinate System 2000(CGCS2000)
The 2000 coordinate system, namely the China Geodetic Coordinate System 2000 (CGCS2000 for short), is a new generation of geocentric coordinate system released by the National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geoinformation of China in 2008, replacing the Xi’an 1980 coordinate system. CGCS2000 adopts the standard of the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) and is highly compatible with the WGS84 coordinate system (the earth coordinate reference system used worldwide). Its geodetic datum is based on the GRS80 ellipsoid (the 1980 International Reference Ellipsoid), with accurate geocentric positioning, and is suitable for various precise measurements and geographic information processing.
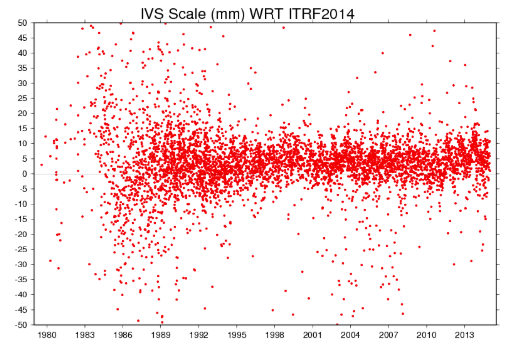
2025-09-16 14:47:05International Terrestrial Reference Frame 2014 (ITRF2014)
ITRF2014 is the latest version of the International Earth Reference Frame. It is built based on multi-technical integrated observation data, providing high-precision earth coordinates and motion parameters, and providing a unified benchmark for geological research, space activities and geodesy.
2025-09-16 14:47:07Geodetic Coordinate System 2002(GCJ-02)
Geodetic Coordinate System 2002, also known as GCJ-02 or nonlinear confidentiality processing technology for topographic maps, is a coordinate system for geographic information systems developed by the China National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geoinformation in 2002. It is an encryption algorithm for longitude and latitude data. By adding random deviations, the real coordinates are encrypted into false coordinates to achieve the confidentiality of geographic information. The Mars coordinate system is widely used in domestic map services, such as Amap and Baidu Maps, which must use this coordinate system to encrypt geographic locations.
2025-09-16 14:47:07
 Service
Service