UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator)
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
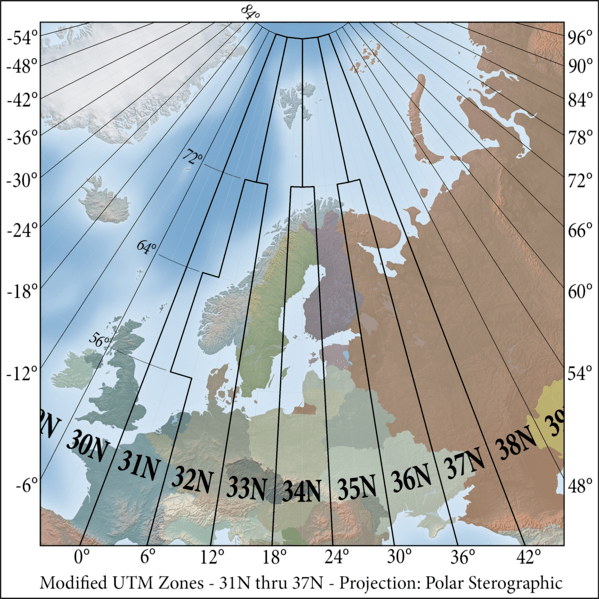
UTM projection (Universal Transverse Mercator) is a coordinate system that divides the earth’s surface into zones and applies the Transverse Mercator projection to each zone. By dividing the earth into 60 zones, each zone is 6 degrees longitude apart, and projecting independently in each zone, high-precision plane rectangular coordinates can be obtained.
Each zone is identified by a zone number with the suffix “N” for the northern hemisphere and “S” for the southern hemisphere, based on the equator. For example, “UTM Zone 54N” is an example of a zone that includes the Kanto region of Japan.
This projection takes into account the curvature of the earth, but it can be regarded as a relatively flat surface within each zone, so it is widely used in fields that require high positioning accuracy, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and GPS.
Projection Composition
UTM coordinate systems are usually recorded in a format that contains the following elements:
1.Easting: distance east from a reference point in the zone (central meridian) in meters
Northing: distance north (or south) from the equator in meters
Zone number (1-60): zone number defined by longitude
Northern or Southern hemisphere designation (N or S)
Many GIS software (such as ArcGIS, QGIS, GISBox, etc.) support UTM projections, and also support formats such as GeoTIFF and Shapefile. Standard EPSG codes are individual EPSG codes for UTM zones (e.g. EPSG:32654 for zone 54N).
Pros
- Extremely high distance, area and angle accuracy for applications such as surveying, construction, and urban planning.
- Accuracy up to meters, simplifying analysis and calculations.
- Widely used, standard configuration for various software and GPS devices.
- Global coverage, while supporting optimized structures by region.
Cons
- Not suitable for wide-area analysis across regions (correction is required when across regions)
- Since each region is independent, unified visualization and calculation across regions need to be cleverly achieved
- There may be a mixture of different northing standards (equatorial standard and 1,000,000-meter offset) in the northern and southern hemispheres
- Not suitable for global display of the entire earth, limited to local high-precision applications
Application Scenario
The UTM projection is very suitable for local geographic information processing that requires accuracy. It is widely used in many fields such as urban planning, architectural design, forest management, road and railway infrastructure construction, disaster prevention mapping, and military surveying. In particular, since GPS devices often output UTM coordinates, it is also often used in site surveys and field investigations.
Example
- UTM zones across Japan.

- UTM zone for Northern Europe.
Related GIS Projections
Lambert Azimuthal Equal-Area Projection