Web Feature Service(WFS)
GISBox is a one-stop 3D GIS data editing, conversion and publishing platform that supports editing in multiple GIS formats such as OSGB/GEOTIFF/RVT, converting to 3DTiles/Terrain and publishing.
Introduction
Web Feature Service (WFS) is a service for online sharing and interoperability of geographic feature data in a network environment. It is based on a distributed computing platform that supports the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and provides functions such as query, acquisition, creation, locking, update, and deletion of geographic features and their attribute data. WFS uses Geography Markup Language (GML) to describe geographic feature data and defines a variety of operations to implement these functions, including GetCapabilities, DescribeFeatureType, GetFeature, LockFeature (LockFeature, which may not be included in some implementations), and Transaction.
Data Format Overview
According to the degree of support for core interfaces, WFS can be divided into the following types:
Basic WFS: must support the three core interfaces of GetCapabilities, DescribeFeatureType, and GetFeature.
XLink WFS: based on Basic WFS, adds support for the GetGmlObject interface.
Transaction WFS (also known as WFS-T): based on Basic WFS, adds support for the Transaction interface, allowing users to perform online editing and transaction processing. In addition, it can also selectively support the GetGmlObject or LockFeature interface.
Pros
1. Standardization and interoperability: WFS follows the OGC (Open Geospatial Consortium) standard to ensure interoperability between different GIS systems.
**2. Real-time data access and update: **WFS provides real-time access to geospatial data, enabling users to obtain the latest geographic information.
**3. Flexible data query and retrieval: **WFS supports common queries based on spatial geometric relationships, attribute domains, and spatial relationships and attribute domains, providing rich query conditions.
4. Scalability: WFS requests are not implemented in SQL, but through Filter XML, which makes it more scalable.
Cons
1. Performance bottleneck: When processing large amounts of geospatial data, WFS may face performance bottlenecks, resulting in slower query and update operations.
**2. Security issues: **WFS services are usually accessed over the Internet, so they may face network security threats such as data leakage and malicious attacks.
**3. Data consistency issues: **Since WFS supports online editing and transaction processing, multiple users may update the same geospatial data at the same time, resulting in data consistency issues.
4. Technical threshold: Using WFS requires IS expertise and technical capabilities, including understanding OGC standards, GML data formats, and the use of WFS interfaces.
Application Scenario
Web Feature Service (WFS) has broad application prospects in many fields such as mapping and data visualization, spatial analysis and decision support, data sharing and interoperability, geographic data editing and management, emergency response and disaster management.
Example
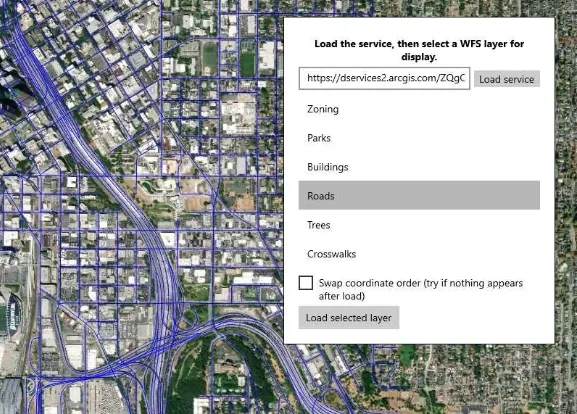
- Web Feature Service.
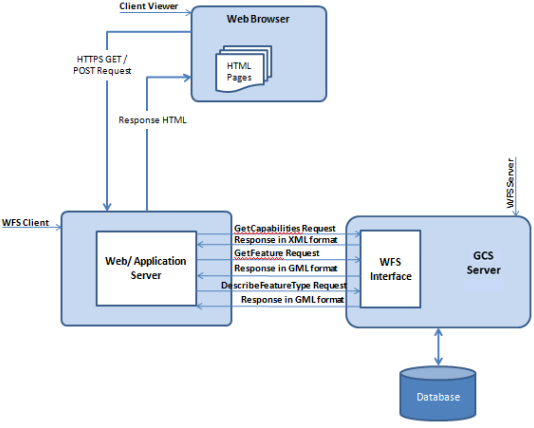
- Example of a WFS response.
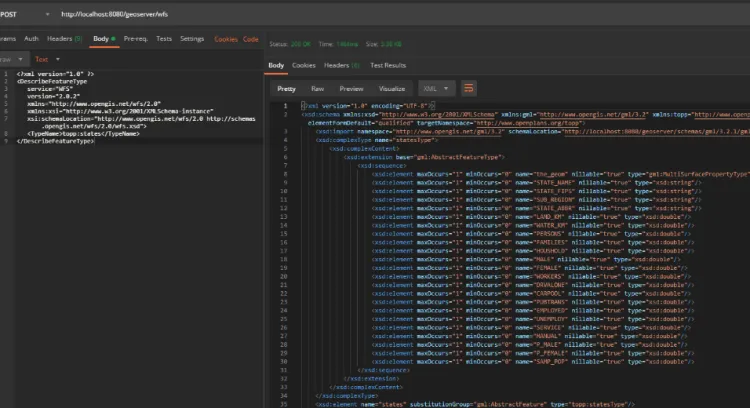
File Opening Mode
1.** **GLoad a WFS using an XML query.
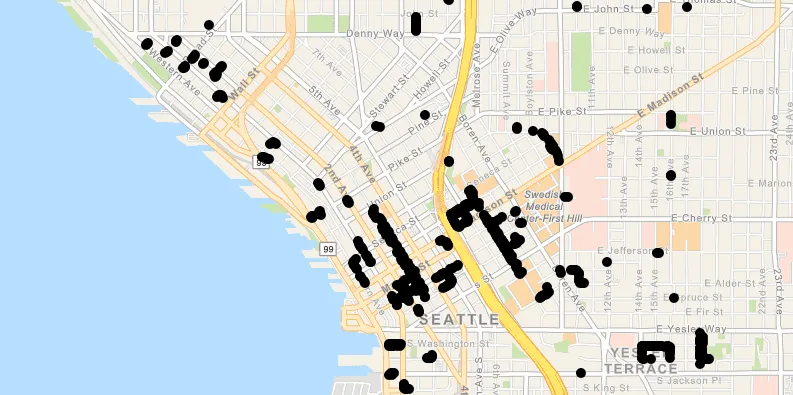
- Open the WFS in ArcGIS.