Patterson Projection
Patterson projection is a compromise cylindrical map projection designed by Tom Patterson. Its structure of equally spaced meridians and symmetrical parallels achieves low distortion in the equatorial region while optimizing the shape of high-latitude regions (superior to the Miller projection). Although it is a non-equal-area projection and only supports spherical models, its visual balance and compatibility with mainstream GIS platforms such as ArcGIS make it widely used in scenarios that do not require precise area calculations, such as education and popular science, time zone display, and thematic mapping of areas around the equator.
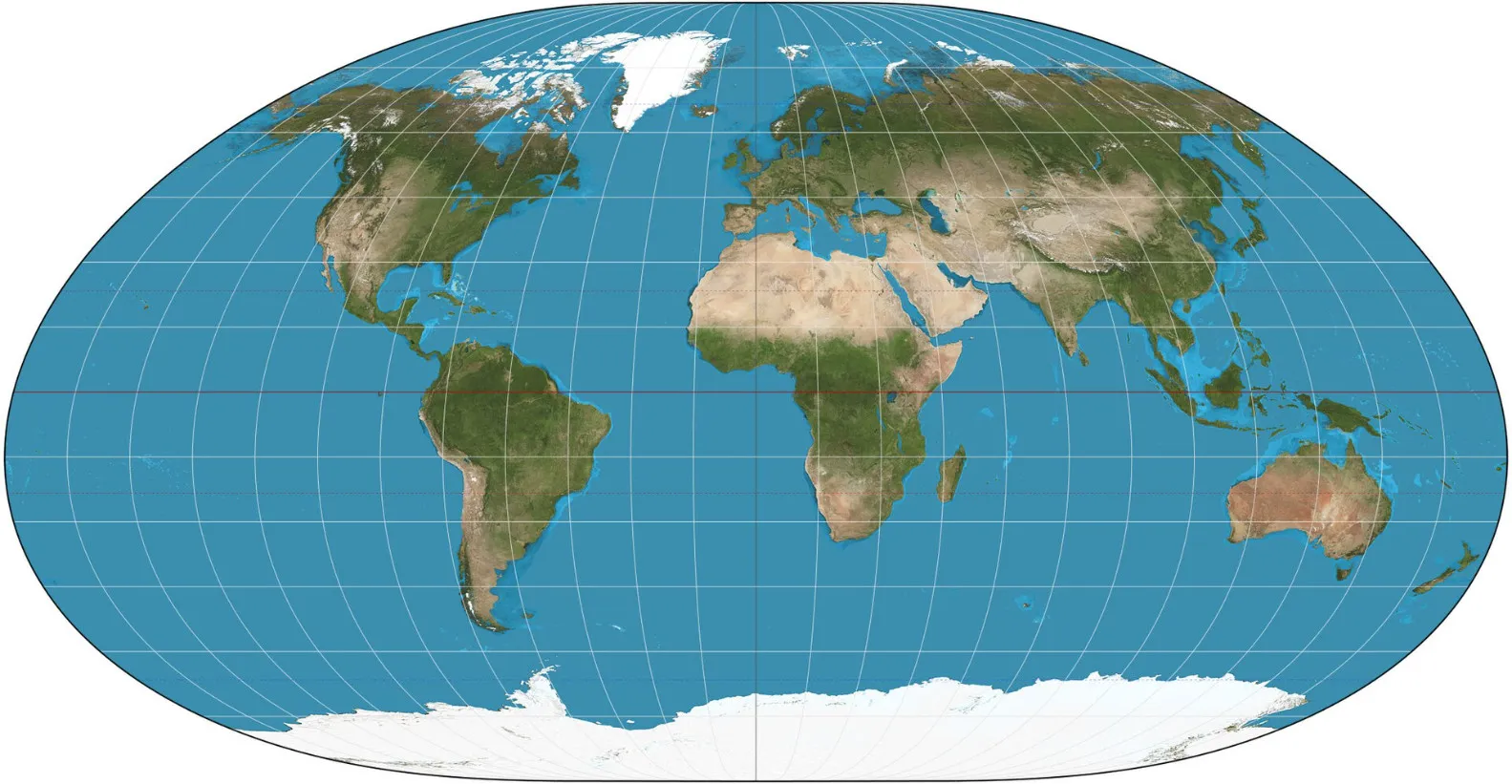
2025-11-05 15:57:26Loximuthal Projection
Loximuthal projection is a pseudocylindrical map projection proposed by Carl Simon in 1935. Its core characteristic is that rhumb lines (loxagonal courses) from a central point (the intersection of the central meridian and the central parallel) are displayed as straight lines, while maintaining true bearing and scale. The projection is neither equal-area nor conformal, but was originally designed to provide accurate compass bearings for maritime navigation while clearly defining local shapes by accurately representing course and distance from a central point.
2025-11-05 15:56:34Hotine Projection
Hotine projection, also known as a specific implementation of the Oblique Mercator projection, is a conformal map projection developed and popularized by British geodesist Martin Hotine in the mid-20th century for his geodetic work in British colonies, primarily in the Malay Peninsula.
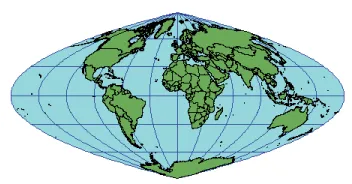
2025-11-05 15:55:24Hammer Aitoff Projection
Hammer projection is a modification of the Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection, also known as the Hammer–Aitoff projection. It was developed in 1892 by German cartographer Ernst von Hammer, who was inspired by the work of Russian cartographer David A. Aitoff and, as such, represents an improvement on the Aitoff projection.
2025-11-05 15:54:36Gall Stereographic Projection
Gall stereographic projection is a cylindrical projection that projects the Earth's surface from a point opposite the equator onto a cylindrical surface, with the standard parallel fixed at 45 degrees. Its characteristics are parallel straight lines and equal-length curves of longitude. The scale is accurate along the standard parallels and remains constant between parallels equidistant from the equator. While it is neither equal-area nor equidistant nor conformal, it balances the scale of mid-latitudes, avoiding excessive stretching at the poles or compression at the equator, while maintaining high shape fidelity.
2025-11-05 15:51:00Craster Parabolic Projection
Craster parabolic projection is a type of map projection classified as a pseudo-cylindrical projection that projects the Earth's surface onto a flat surface in a manner that approximates the shape of a parabola. This method was invented by John Craster in 1910 and is primarily used to create world maps. The map's parallels are straight and evenly spaced, while the meridians, except for the central meridian, are parabolic. It achieves a relatively smooth visual balance while minimizing area distortion, making it suitable for educational materials and visually easy-to-understand globe displays.
2025-11-05 15:47:48Berghaus Star AAG
Berghaus Star Projection is a unique map projection that divides the entire surface of a globe into a star shape. It was invented in the 19th century by German geographer Hermann Berghaus and has been used primarily for decorative or educational purposes due to its beauty and unique composition. The variation used by the American Association of Geographers (AAG) in particular is known as an iconic design in geography.
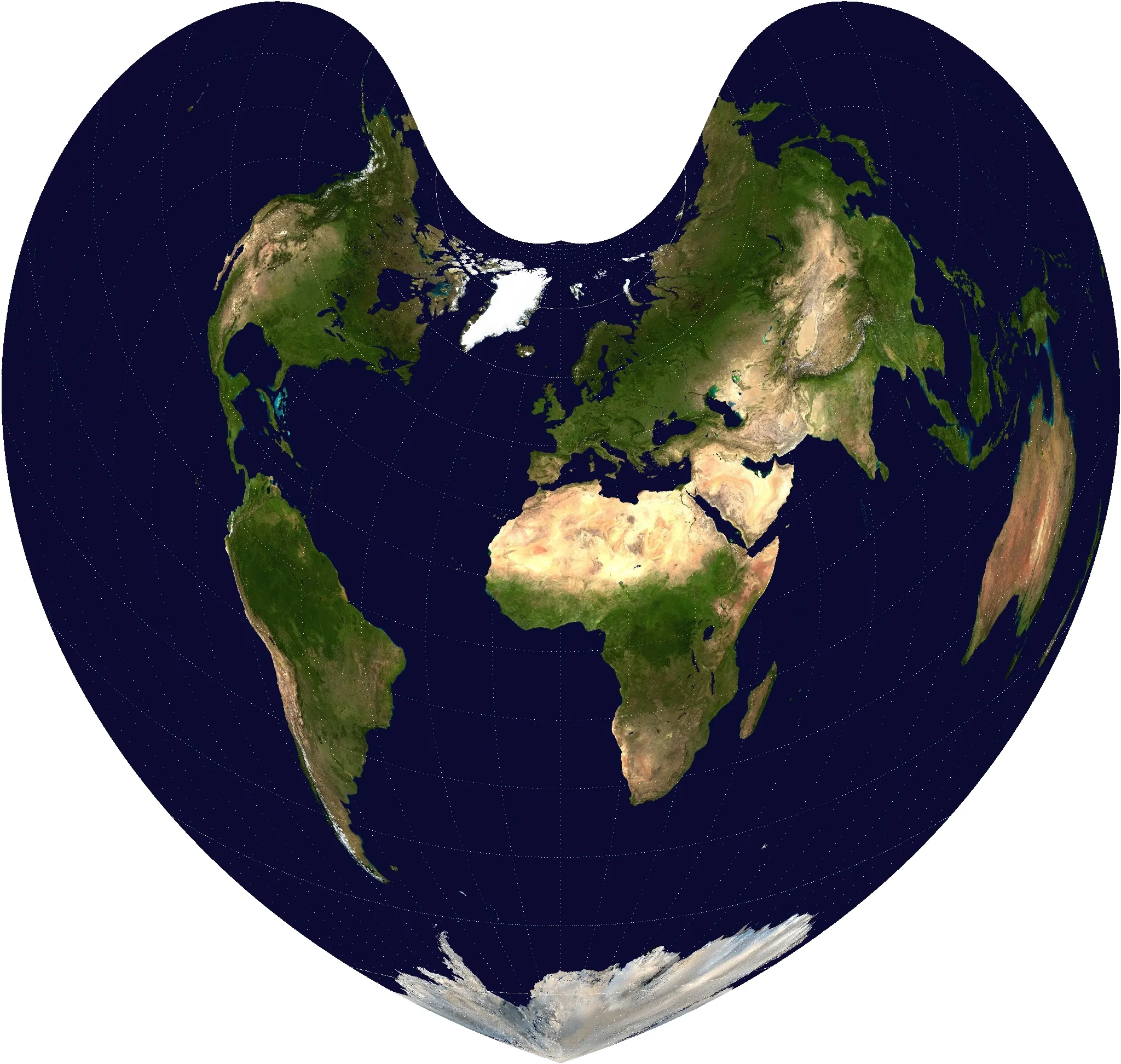
2025-11-05 15:47:03Bonne Projection
Bonne Projection is a type of pseudo-conic projection in which all parallels are represented as concentric circular arcs, and meridians are drawn radiating from a central parallel. It was once widely used in the fields of geography and surveying because it minimizes distortion of area and shape at specific reference parallels (standard parallels). A distinctive feature of this projection is that the resulting map appears as a large heart, and it has historically been used for producing maps of countries and continents, particularly those of Europe.
2025-11-05 15:46:05Cassini Projection
Cassini Projection is a type of equilateral transverse Mercator projection devised by the Italian astronomer Jacques Cassini in the 18th century, and is intended to accurately represent areas along the central meridian. It is suitable for mapping elongated areas oriented north-south because it causes little distortion of shape and distance on and around the central meridian. However, distortion of shape and area increases the further away from the central meridian. Historically, it was used for many land surveys and military maps in the 19th century.
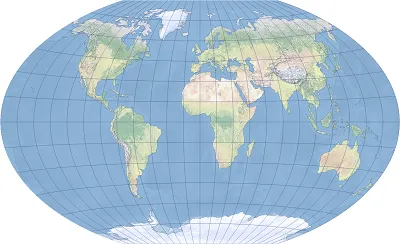
2025-11-05 15:44:00Winkel Tripel Projection
Winkel Tripel Projection is a map projection developed with the goal of projecting geographic information as balanced as possible on a map. It was invented by German geographer Oswald Winkel in 1921 and is a combination of the Equirectangular Projection and the Aitoff Projection. The name "Tripel" comes from the fact that distortions of latitude and longitude, area, and distance are kept to a "triple" level. It is used in many countries' atlases and educational materials to achieve a balanced appearance when displaying world maps.
2025-11-05 15:43:10
 Service
Service

_1762329480207.png)
_1762329353567.png)
_1762329312411.jpg)
_1762329088768.png)
_1762328853812.png)